Flowers are an attractive and significant part of the plant. They are nature's way of ensuring that plants can reproduce and create new generations.
Along with their cultures and symbols of beauty, love, and various emotions, flowers also play a crucial role in plant reproduction and ecosystems.
Yes. Flowers are the reproductive system of plants.
Just like humans and animals, plants have different reproductive organs that play a significant role in reproduction, which is the sole function of flowers.
Understanding the different parts of a flower, from the petals to the sepals, the stamens to the pistils, and other reproductive organs, plays a vital role in learning about reproduction, pollination, seed production, and much more.
In this article, we will explore the significant reproductive parts of a flower in detail and discover how they work together to maintain the plant’s life cycle.

The flower is the reproductive unit in all flowering plants. It is meant for sexual reproduction.
The complete process of flowering is carried out in three different stages:
Plants are divided into two categories based on how they bear flowers.
A plant that bears flowers and fruits is called a flowering plant or angiosperm.
Rose, Hibiscus, Marigold, Jasmine, Portulaca and Adenium are some examples of angiosperms, or flowering plants.
Non-flowering plants are those plants which do not produce flowers or fruits and seeds, as they lack specialised reproductive organs. These plants are called cryptogams. Ferns, mosses, liverworts, horsetails, and gymnosperms like conifers and cycads are a few examples of non-flowering plants.
A typical flower has four different kinds of whorls arranged successively on the swollen end of the stalk or pedicel, called the thalamus or receptacle.
These four kinds of whorls are: calyx, corolla, androecium, and gynoecium.
The calyx and corolla are accessory organs, while the androecium and gynoecium are reproductive organs.
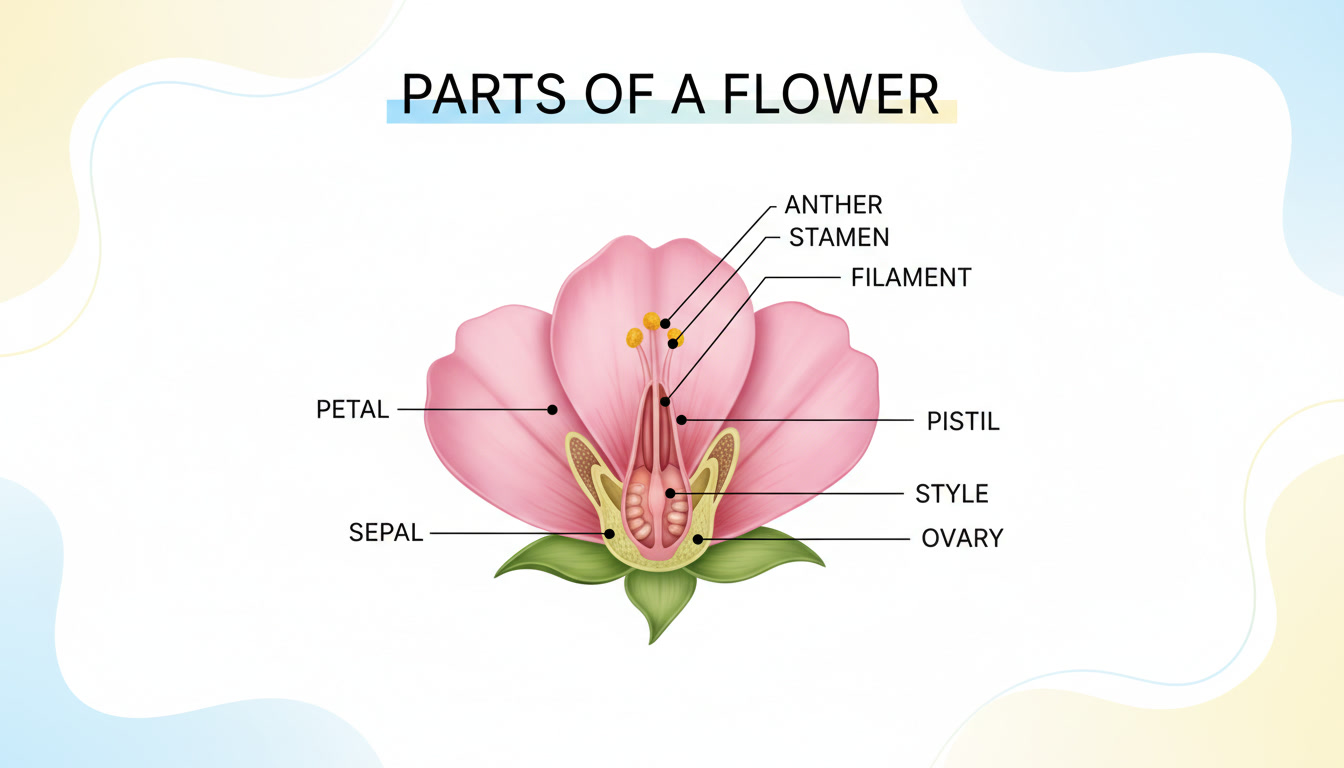
Here is a Diagram of a Flower:
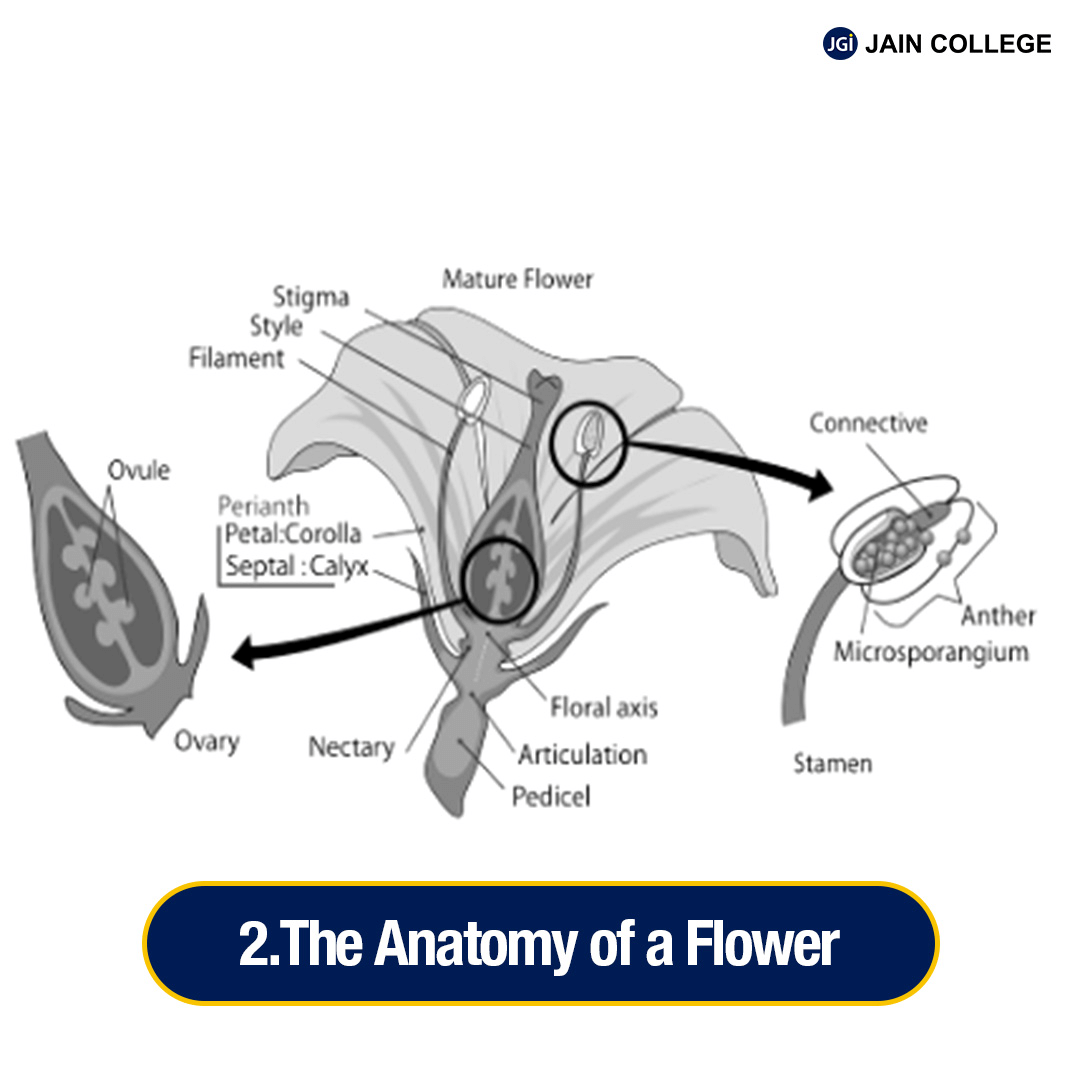
Let us learn in detail about the different parts of flowers along with their functions:
The flower’s anatomy is intricately designed to ensure the success of pollination and reproduction, which in turn ensures the survival of the plant species.
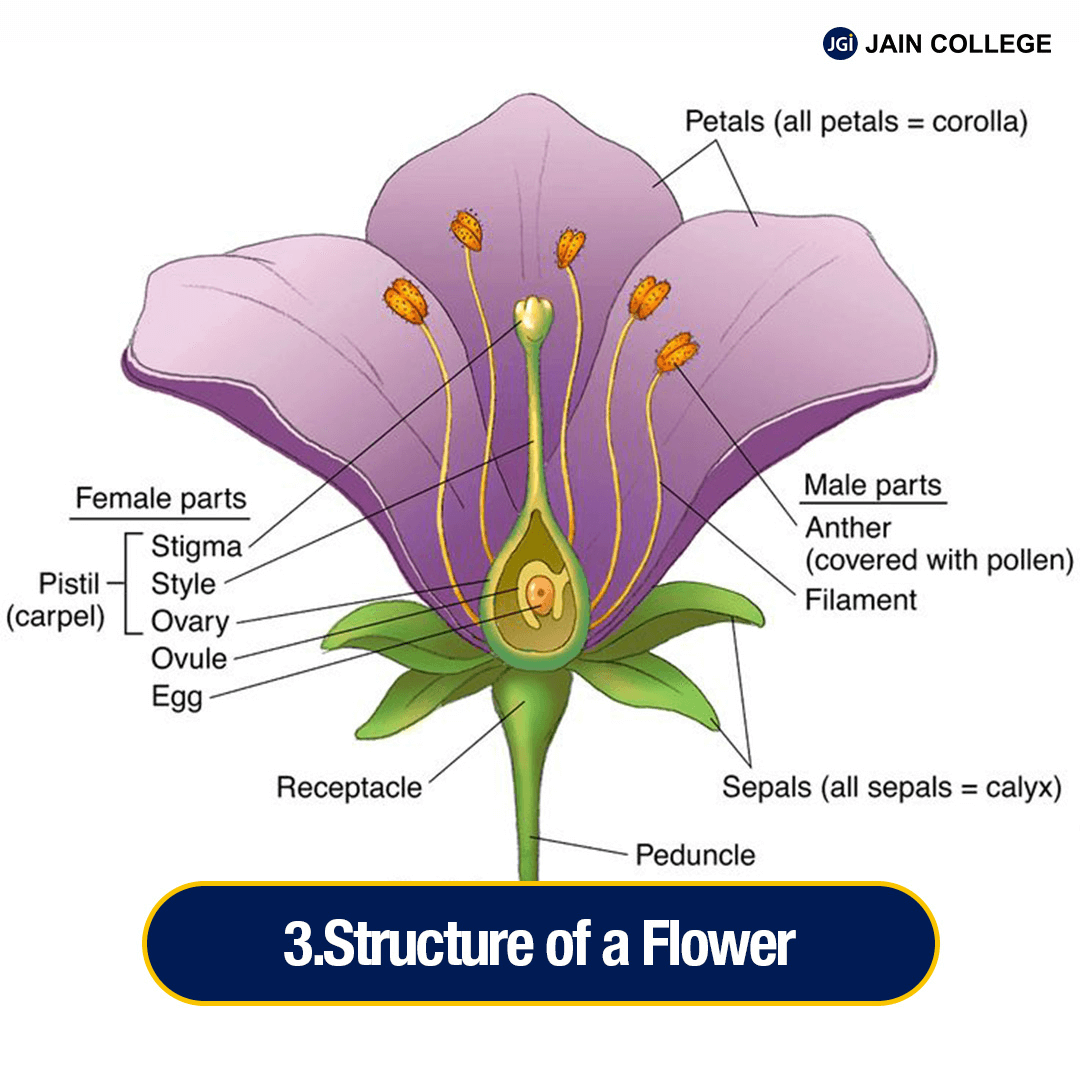
The structure of a flower is carefully organised to support its complete reproduction process.
Here is an overview of the main parts of a typical flower and their structure:
The structure of a flower is specifically designed to support its role in reproduction—from attracting pollinators to producing seeds. The different parts of a flower function together to facilitate pollination, fertilisation, and seed development, which are essential for the continuation of plant species.
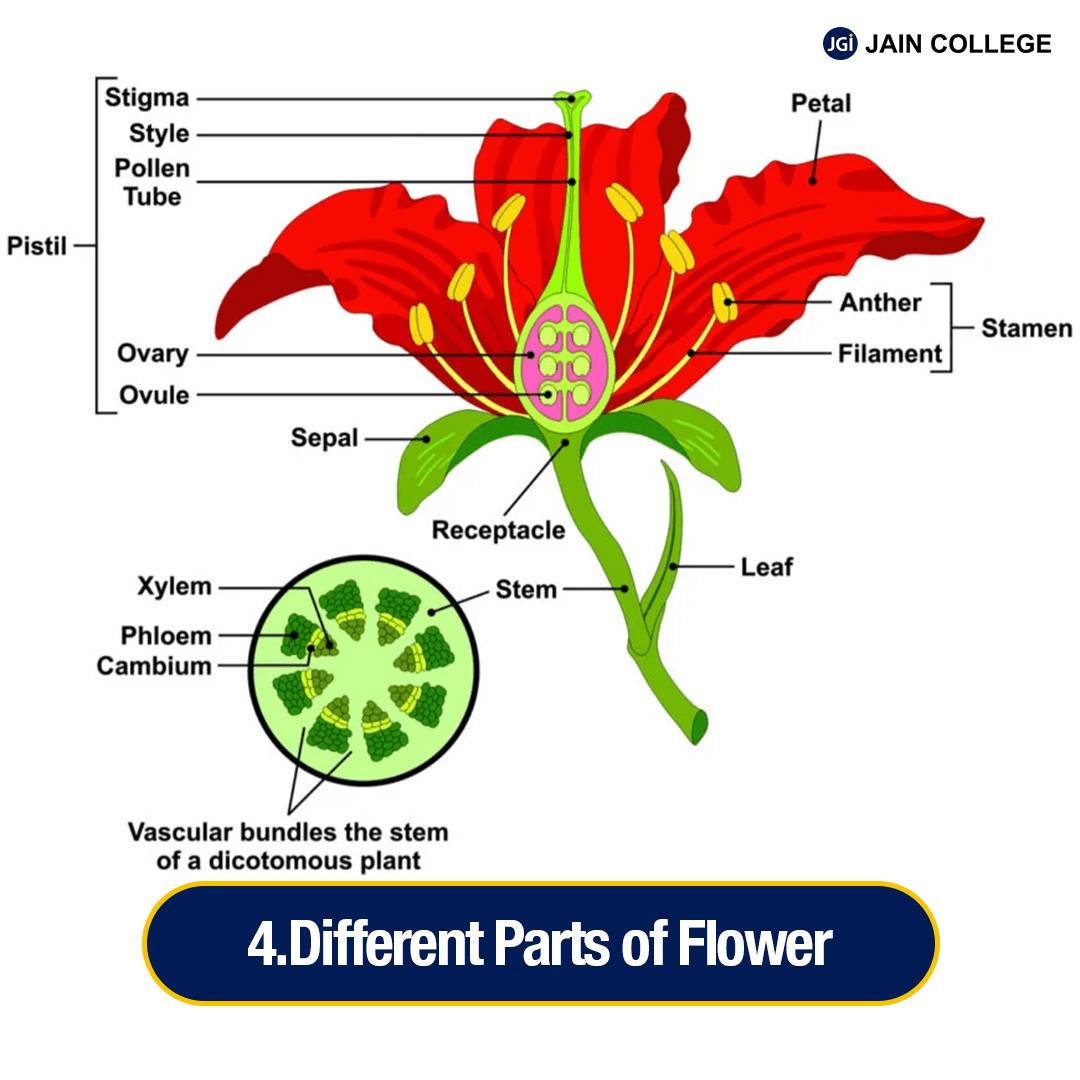
The anatomy of a flower consists of several key parts, each serving a specific function to ensure the plant’s reproduction.
Here is a breakdown of the primary parts of a flower, their descriptions and their functions:
| Parts of a Flower | Description | Functions |
| Peduncle | The peduncle holds the flower upright and connects it to the plant | The stem that supports the flower |
| Receptacle | It is the thickened part of the stem at the base of the flower | It comprises floral organs (petals, sepals, stamens, and pistils), which are attached |
| Sepals | Sepals are green, leaf-like structures that encircle the base of the flower. Together, they form the calyx | Protect the developing flower bud before it opens |
| Petals | Petals are often brightly coloured and form a corolla. They help guide pollinators like bees and butterflies toward the reproductive parts of the flower | Attract pollinators with their colour, shape, and fragrance |
| Stamens | The stamens are the male reproductive part of a flower. It consists of a filament and anther Collectively, all the stamens of a flower are called the androecium | Produce pollen, which contains the male gametes (sperm cells) |
| Anther | The top part of the stamen | Produce pollen |
| Filament | A long slender stalk, with a two-lobed anther at the tip | Supports the anther and positions it for optimal pollen dispersal |
| Pistil | The pistil is the female reproductive part of a flower. The pistil consists of three main parts: Stigma, Style and Ovary. Collectively, all the pistils of a flower are called the gynoecium | Receives pollen and facilitates fertilisation of the ovules (egg cells) |
| Stigma | The sticky surface present at the top of the pistil | It captures and holds pollen |
| Style | The stalk that supports the stigma and connects it to the ovary | Mediates pollination by providing a transmitting tissue for the pollen tube |
| Ovary | The ovary is typically located at the base of the pistil and holds the plant's female reproductive cells (ovules) | Contains the ovules, where fertilisation takes place, leading to seed formation |
| Ovules | Are found within the ovary. After fertilisation, they become seeds that can grow into new plants | Contain the egg cells that, after fertilisation, develop into seeds |
| Nectary | It is typically located at the base of the flower, often hidden inside the Flower structure. It secretes a sugary liquid that encourages pollinators to visit | Produces nectar for pollination |
These are the different parts of the flower that work together to ensure pollination and the production of seeds, allowing the plant species to continue.
A flower is an essential part of a plant; it performs a crucial role in reproduction and continues its life cycle.
The beautiful flower petals attract pollinators, while the pistils and stamen play a crucial role in fertilisation. Thus, every part of the flower contributes to the plant’s existence.
Understanding the different parts of a flower provides you a more profound understanding of how flowers help plants grow, spread, and continue their life cycle.
Next time you see a flower, remember that it is not merely a beautiful sight. It plays a crucial role in nature's grand design!
For more information on the different parts of flowers, diagrams, and their functions, visit our blogs at https://www.jaincollege.ac.in/blogs
Enrol in JAIN College for top-notch Science, Commerce, and Arts programmes. Secure your path to success today!
The flower is the reproductive unit in angiosperms, or flowering plants. It plays a primary role in sexual reproduction, the biological life process.
Sepals are small, green, leaflike structures located at the base of a flower. They protect the flower buds.
The stamen is the male reproductive organ of a flower.
The calyx is the outermost whorl of the flower.
The stamen is the male reproductive part or organ of a flower. The pistil is the female reproductive part or organ of a flower.
The carpel and pistil are both the female reproductive parts of a flower.
The carpel generally consists of an ovary, stigma, and style, while the pistil consists of several carpels.
The stamen comprises a pollen sac (anther) and a long supporting filament. This filament holds the anther in position, making the pollen available for dispersal by wind, insects, or birds.
The pistil is a female reproductive organ that helps reproduce in all flowering plants. It is centrally located and comprises the stigma, style, and ovary.
The four processes of reproduction in flowering plants are:

JAIN PU College, a part of the renowned JGI Group, is committed to empowering students with quality education.
Beyond academics, the college ensures its online content reflects the same standard of excellence. Every blog and article is meticulously vetted and proofread by subject matter experts to ensure accuracy, relevance, and clarity. From insightful educational topics to engaging discussions, JAIN PU College's content is crafted to inform, inspire, and add value to its readers, reflecting the institution's commitment to intellectual growth and innovation.
View all Blogs