
In our gardens, schools, colleges, parks, near the roadside, in valleys, deserts, and fresh and saltwater—almost everywhere on the planet—we encounter various plants in various shapes and sizes.
Do all these plants have basic structures, or do they differ in their parts?
Yes. Like humans and animals, plants have specialised parts, each with a unique function. All plants share parts that help them grow, reproduce, and survive. Learning these parts helps us understand how plants contribute to the ecosystem and our daily lives.
In this article, we will explore the different parts of the plant through a diagram and discover how each part works together to help the plant grow and reproduce.
Plants are fascinating organisms that play a crucial role in our environment. They are essential for life on Earth.
Plants are made up of several parts, each with a specific function. The main parts of a plant include the roots, stem, leaves, flowers, and fruits. Each part helps the plant survive and grow.
Explore the parts of the plant!
Here is the diagram showcasing the parts of plants:
Roots are like the plant's anchor and lifeline. They hold the plant in place and absorb water and nutrients from the soil.
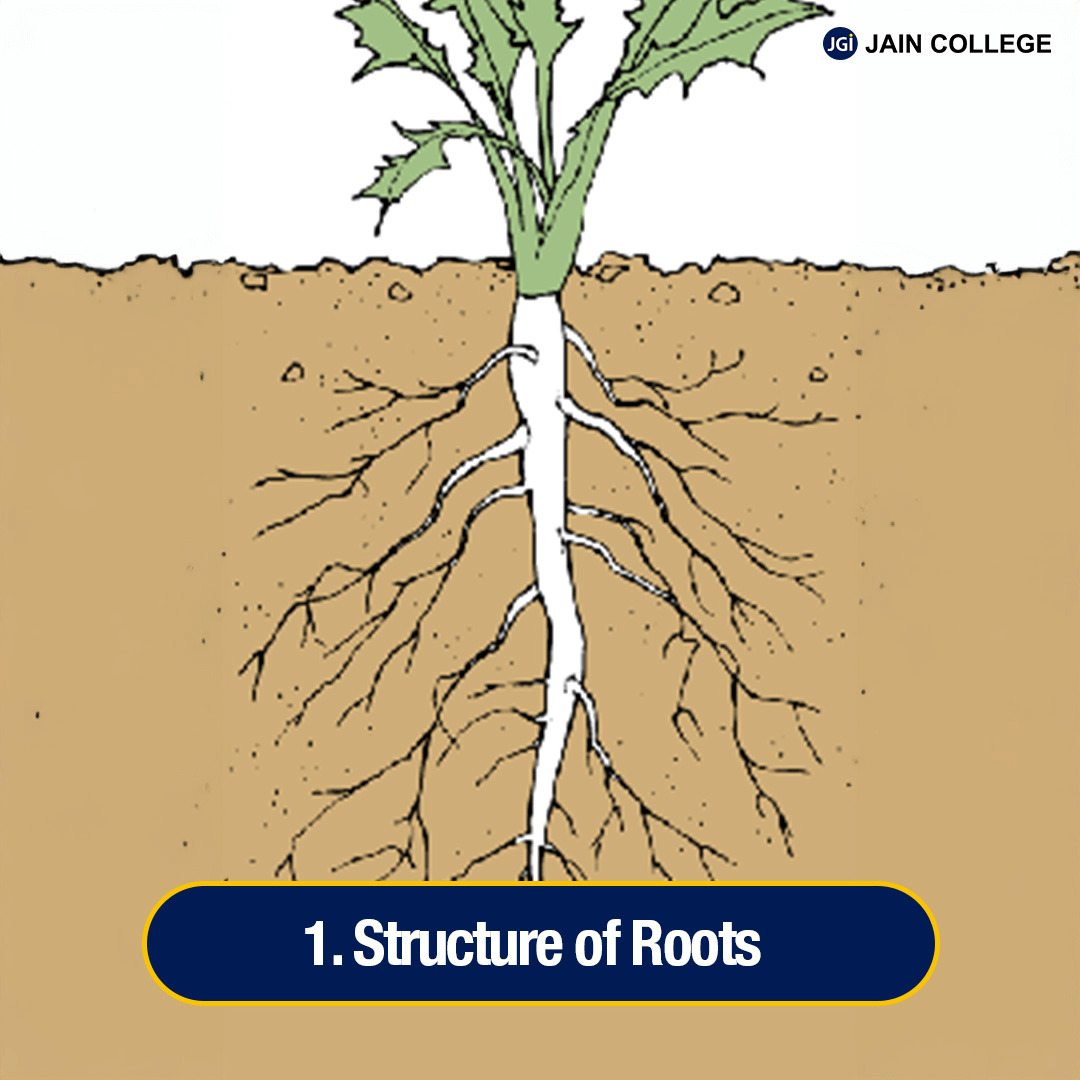
Roots have different parts:
The stem is the ascending part of the axis bearing branches, leaves, flowers and fruits. It develops from the plumule of the embryo of a germinating seed.
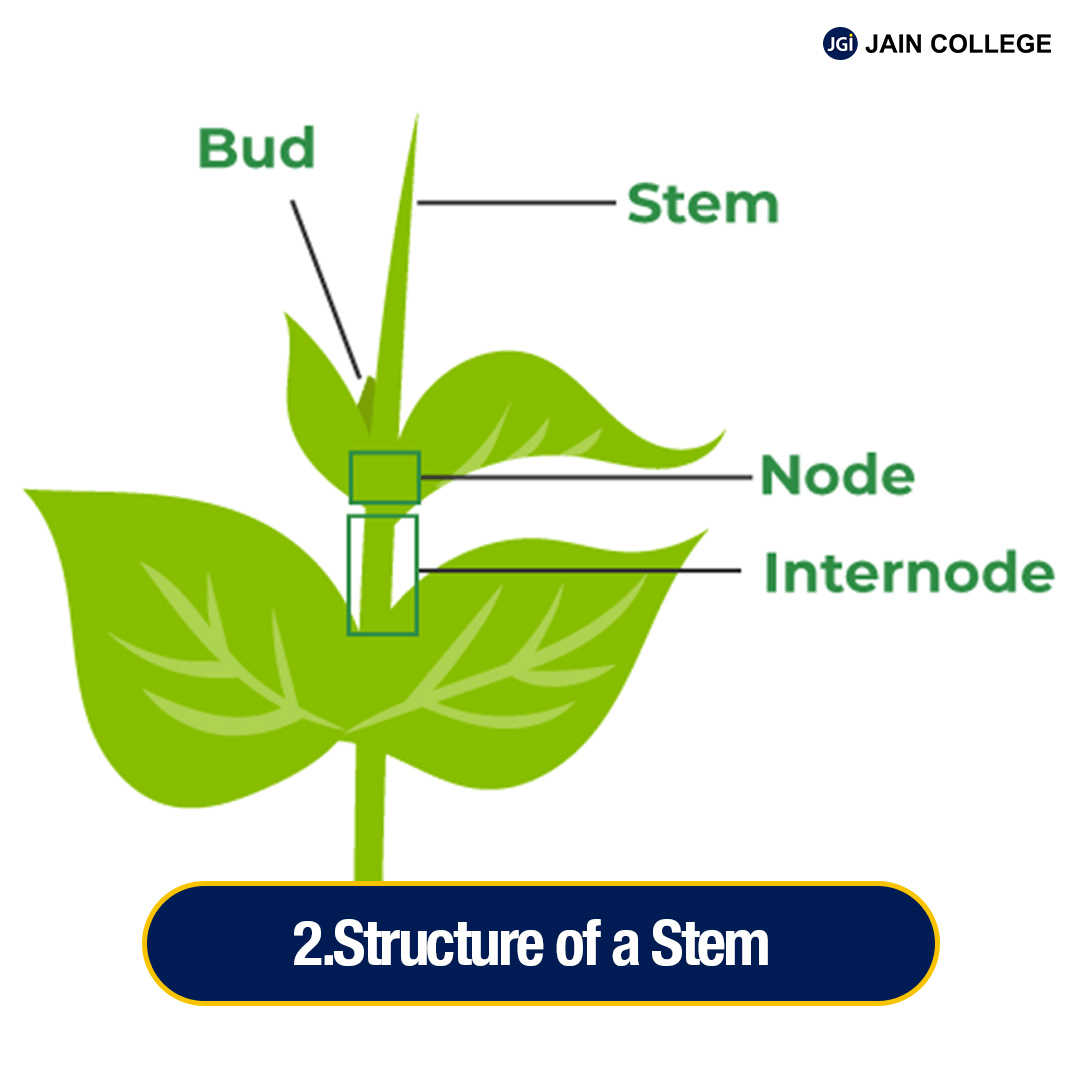
Stem is generally green when young and later often becomes woody and dark brown. The stem bears nodes and internodes. The stem bears buds, which may be terminal or axillary. Other parts of a stem include:
The leaf is a lateral, generally flattened structure borne on the stem. It develops at the node and bears a bud in its axil. Leaves originate from shoot apical meristems and are arranged in an acropetal order.
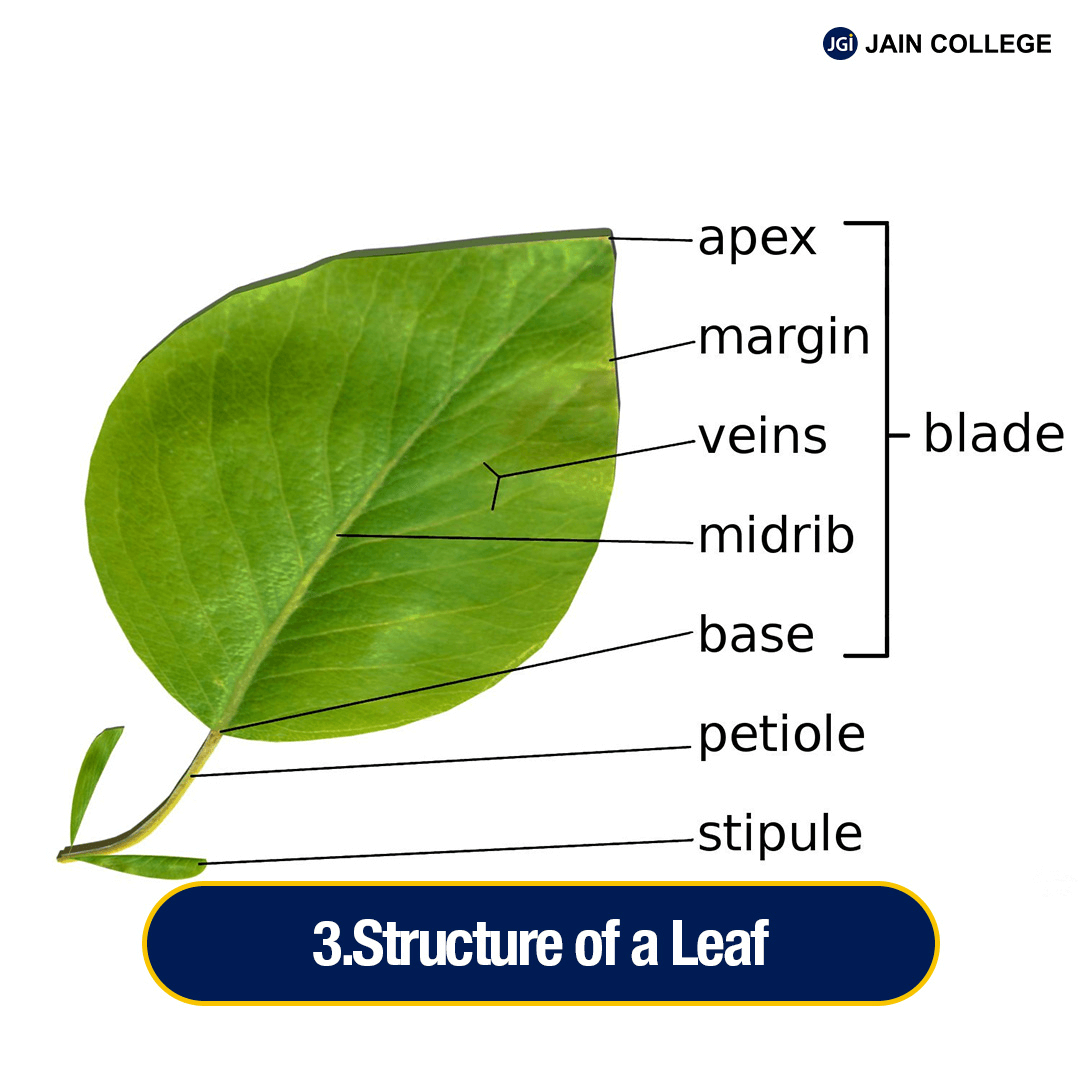
A typical leaf consists of three main parts: Leaf base, petiole and lamina.
The flower is the reproductive unit in the angiosperms. It is meant for sexual reproduction.
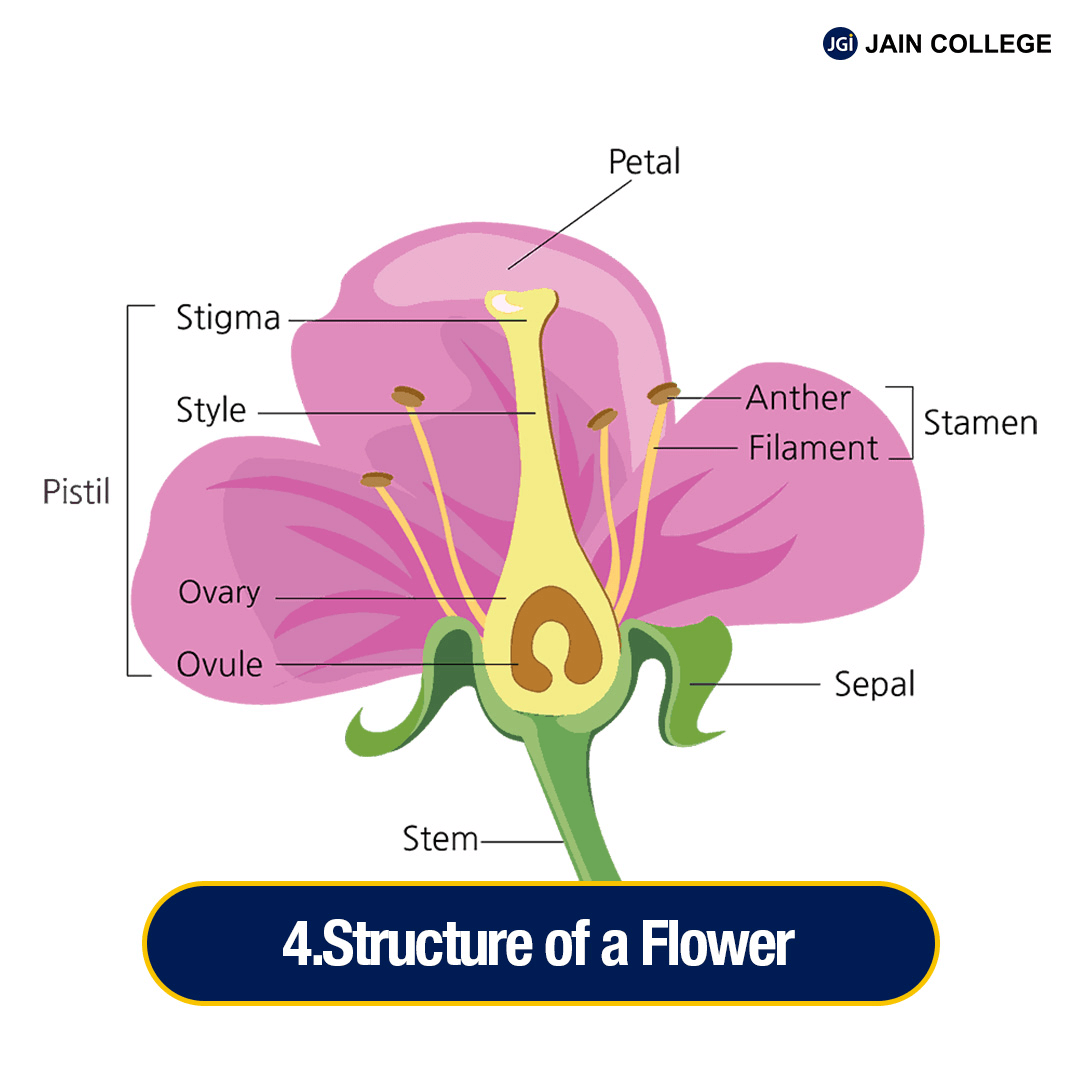
A typical flower has four floral whorls: calyx, corolla, androecium and gynoecium.
Androecium: The androecium is the male reproductive part of a flower. It is composed of stamens.
Gynoecium
The gynoecium is the female reproductive part of the flower and is composed of one or more carpels.
Fruit is a characteristic feature of flowering plants. Fruits are formed when a mature or ripened ovary develops after fertilisation. The fruit contains seeds that can grow into new plants.
If a fruit is formed without fertilisation of the ovary, it is called a parthenocarpic fruit.
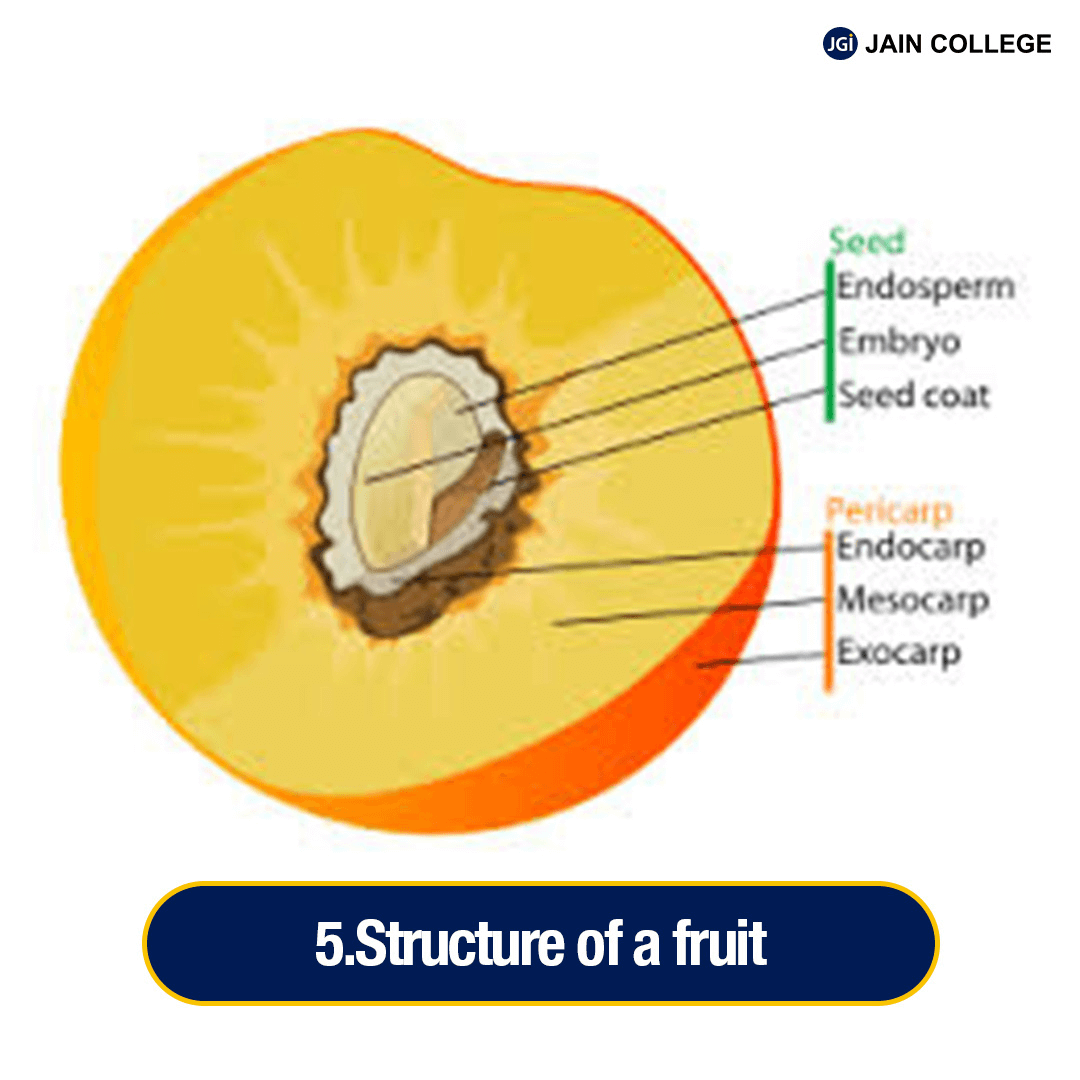
The fruit generally consists of :
Thus, each part of the plant functions together to help it grow, reproduce, and survive.
| Roots | The roots keep it grounded and nourished |
| Stem | The stem provides structure and support |
| Leaves | The leaves prepare food |
| Flowers | The flowers help in the reproduction process |
| Fruits | The fruits help in seed dispersal |
Also Read: Parts of a Flower
The parts of a plant are all interconnected and play an essential role in the plant’s growth, reproduction, and overall survival.
Each part plays a vital role, from the roots that anchor the plant to the soil to the leaves that carry out photosynthesis and the flowers that allow the plant to reproduce.
By learning about these parts, we gain a more profound gratitude for the natural world around us and understand how plants contribute to our environment and support life on Earth.
For more information on the different parts of flowers, diagrams, and their functions, visit our blogs at https://www.jaincollege.ac.in/blogs.
Join JAIN College for top-notch Science, Commerce, and Arts programmes. Secure your path to success today!
The root system is the plant axis's descending (growing downwards) portion.
The shoot system is differentiated into stems, leaves, flowers and fruits.
The leaf is a lateral outgrowth of a stem developed exogenously at the node.
The flower is a modified shoot meant for sexual reproduction.
Inflorescence refers to the process of arrangement of flowers on the floral axis.
A seed is a part of a plant that is developed after the fertilisation of ovules. When planted, seeds can grow into a new plant.
A seed is composed of a seed coat and an embryo.
Parthenocarpic fruits are a type of fruit formed without the ovary's fertilisation.
Plants play a primary and essential role as a food source and provide many other products, including medicines and raw materials, to produce various industrial products, including paper, spices, cosmetics, ornamentals, pencils, rubber, furniture, and other household products.

JAIN PU College, a part of the renowned JGI Group, is committed to empowering students with quality education.
Beyond academics, the college ensures its online content reflects the same standard of excellence. Every blog and article is meticulously vetted and proofread by subject matter experts to ensure accuracy, relevance, and clarity. From insightful educational topics to engaging discussions, JAIN PU College's content is crafted to inform, inspire, and add value to its readers, reflecting the institution's commitment to intellectual growth and innovation.
View all Blogs