List of Shapes and Symbols
| Shapes |
Symbols |
| Circle |
 |
| Rectangle |
 |
| Pentagon |
 |
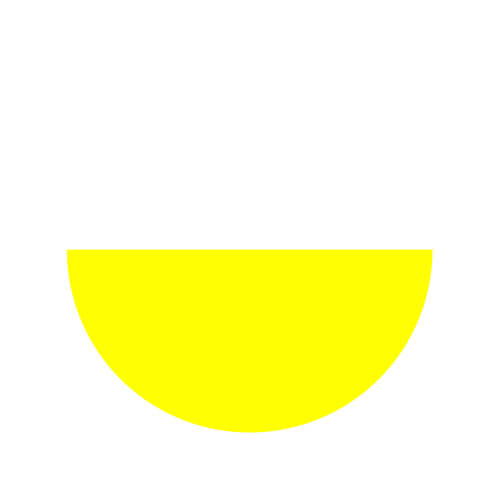
| Semi Circle |
 |
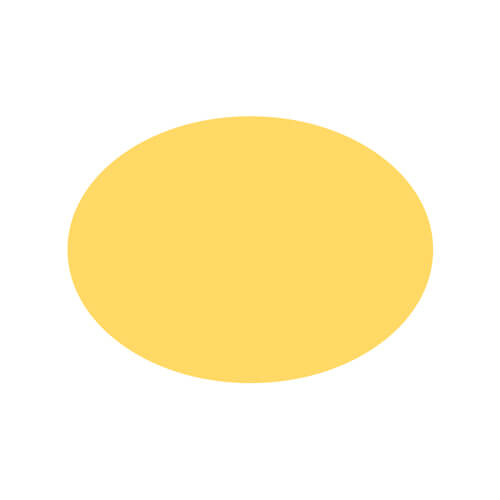
| Oval |
 |
| Square |
 |
| Diamond |
 |
| Right Triangle |
 |
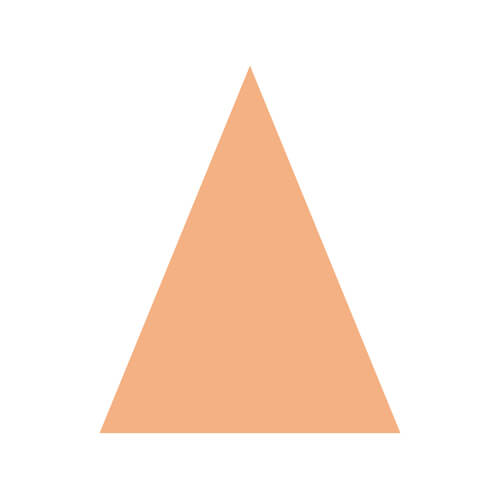
| Isosceles Triangle |
 |
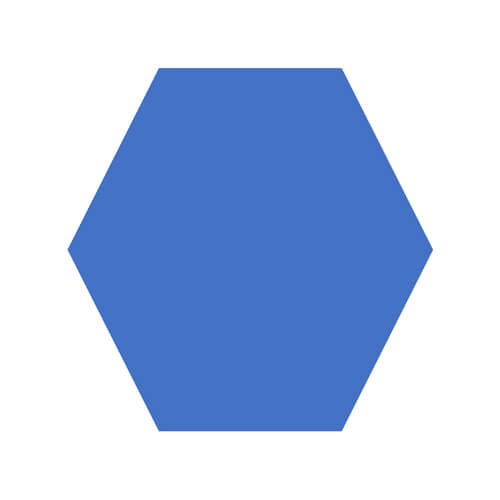
| Hexagon |
 |
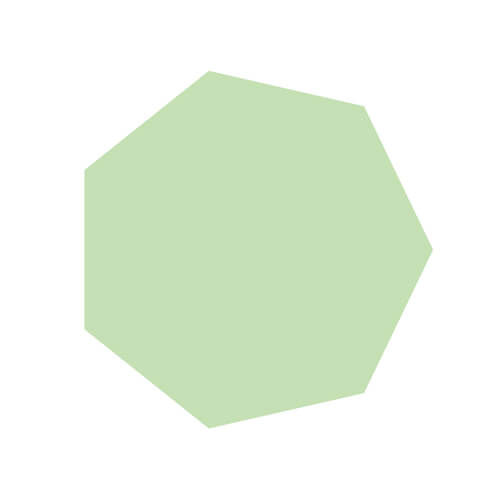
| Heptagon |
 |
| Decagon |
 |
| Dodecagon |
 |
| Parallelogram |
 |
| Cylinder |
 |
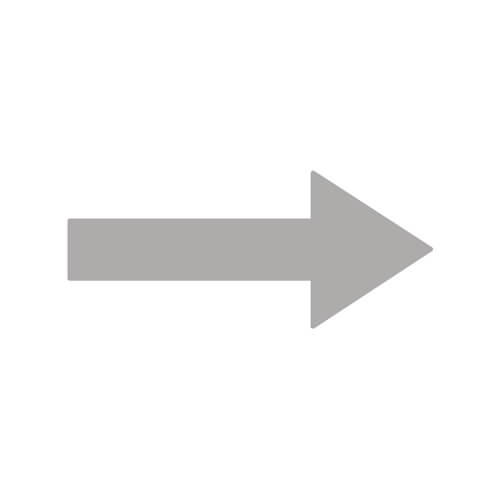
| Arrow |
 |
| Cube |
 |
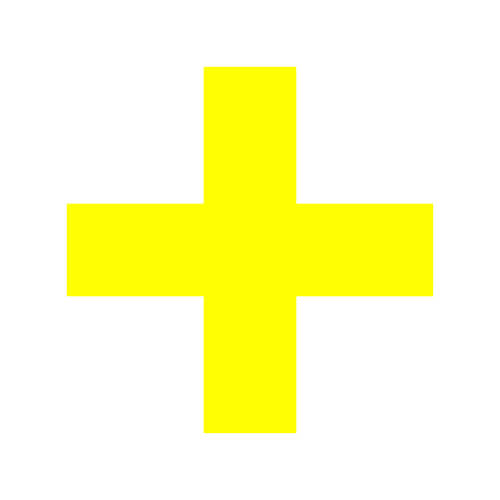
| Plus |
 |
| Cuboid |
 |
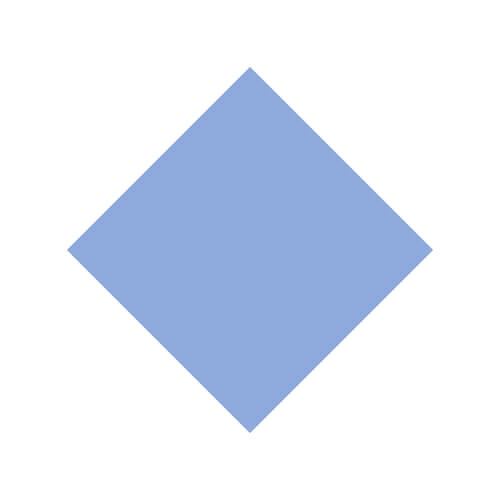
| Rhombus |
 |
| Cross |
 |
| Octagon |
 |
| Star |
 |
| Trapezoid |
 |
| Heart |
 |
| Triangle |
 |
| Crescent |
 |
| Minus |
 |
| Multiplication |
 |
| Division |
 |
What Are Shapes?
At the most basic level, shapes are figures or forms that are the building blocks of the world around us. These can be simple, such as circles and squares, or more complex, like polygons with multiple sides. Whether 2D or 3D, shapes define the boundaries of objects and give them their structure. From a child learning their first words to an engineer designing a bridge, shapes are essential in every stage of life.
Types of Shapes
1. Two-Dimensional (2D) Shapes
These shapes lie flat on a plane and have only length and width.
- Triangle: A shape with 3 sides and 3 angles (e.g., equilateral, isosceles, scalene).
- Square: A polygon with 4 equal sides and 4 right angles.
- Rectangle: A polygon with 4 sides and 4 right angles, opposite sides are equal.
- Circle: A round shape with no sides, where all points are equidistant from the center.
- Pentagon: A shape with 5 sides and 5 angles.
- Hexagon: A shape with 6 sides and 6 angles.
- Octagon: A shape with 8 sides and 8 angles.
- Oval (Ellipse): A stretched or elongated circle.
2. Three-Dimensional (3D) Shapes
These shapes have depth in addition to length and width.
- Cube: A 3D shape with 6 equal square faces.
- Cuboid (Rectangular Prism): A 3D shape with 6 rectangular faces.
- Sphere: A perfectly round 3D shape like a ball, with every point on the surface equidistant from the center.
- Cylinder: A 3D shape with two circular bases and a curved surface connecting them.
- Cone: A 3D shape with a circular base that narrows smoothly to a point.
- Pyramid: A 3D shape with a polygonal base and triangular faces that meet at a point.
- Tetrahedron: A type of pyramid with a triangular base, having 4 triangular faces.
3. Curved Shapes
These shapes feature curves rather than straight lines.
- Ellipse: A closed, oval-shaped curve, like a stretched circle.
- Parabola: A U-shaped curve, typically seen in graphs of quadratic equations.
- Hyperbola: A set of two mirrored, open curves.
4. Regular and Irregular Shapes
- Regular Shapes: Shapes with all sides and angles equal (e.g., square, equilateral triangle).
- Irregular Shapes: Shapes where sides and angles are not equal (e.g., scalene triangle, irregular polygon).
5. Complex Shapes
- Composite Shapes: Shapes formed by combining multiple basic shapes (e.g., a house shape made from a rectangle and a triangle).
Why Is It Important to Learn Shape Names?
Understanding shape names goes beyond recognizing objects. It enhances cognitive development, spatial reasoning, and critical thinking skills. For children, learning shapes helps in visual discrimination and the ability to categorize objects based on their properties. For adults, recognizing shapes is vital in areas such as architecture, art, and mathematics, where precision and design are key.
List of 2D Shapes
| Shape Name |
| Circle |
| Triangle |
| Square |
| Rectangle |
| Pentagon |
| Hexagon |
| Heptagon |
| Octagon |
| Nonagon |
| Decagon |
| Hendecagon |
| Dodecagon |
| Trapezoid (US) / Trapezium (UK) |
| Parallelogram |
| Rhombus |
| Kite |
| Ellipse |
| Star |
| Crescent |
| Heart |
| Oval |
| Annulus |
| Sector |
| Semicircle |
| Isosceles Triangle |
| Equilateral Triangle |
| Scalene Triangle |
| Right-angled Triangle |
| Quadrilateral |
| Polygons (General term) |
Common Shapes
Here are some names of standard 2D and 3D shapes:
2D Shapes
- Circle: A circle is a shape with no corners or edges; all its points fall equidistant from the centre. It is more commonly seen in coins or cars' wheels.
- Square: A shape in which there are four equal sides and four equal right angles is called a square. Examples can be seen in chess boards, floor tiles, some window panes, etc.
- Triangle: A shape with three sides and three angles, which can be further divided into an equilateral triangle with all sides equal, an isosceles triangle with two sides equal, and a scalene triangle with no sides equal. You can see an example of a triangle shape in a pizza slice or the mountain tops.
- Rectangle: This shape has opposite sides equal in length and, like a square, four right angles. Some common examples are doors, books, etc.
- Polygons: These are considered more advanced geometric shapes. They are multi-sided and have straight edges. Some common polygons include a pentagon with five sides and a hexagon with six sides.
- Oval: Imagine a stretched circle. An oval is just an elongated round shape with two focal points and an unequal distance to the edge. An egg is a classic example of an oval shape.
- Rhombus: The shape of a rhombus resembles a tilted square, but the angles are not right angles like squares. It is a quadrilateral with all four sides equal. Examples are the shape of a kite or a diamond.
- Parallelogram: This 2D shape has opposite sides that are parallel and equal. Rectangles and rhombuses are considered examples of this shape and can also be found in various art and engineering applications.
- Trapezoid: Also known as a trapezium, this quadrilateral has at least one pair of parallel sides called bases, and the opposite sides are called legs. Certain handbags and rooftops are made in the shape of a trapezoid.
All mathematical operators, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication and division, are also considered 2D shapes.
List of 3D Shapes
| Shape Name |
| Sphere |
| Cube |
| Cuboid |
| Cylinder |
| Cone |
| Pyramid (Triangular, Square, Pentagonal) |
| Tetrahedron |
| Octahedron |
| Dodecahedron |
| Icosahedron |
| Torus |
| Prism (Rectangular, Triangular) |
| Ellipsoid |
| Hemisphere |
| Truncated Cone |
| Frustum |
| Parallelepiped |
3 D Shapes
- Cube: It is like a 3D square with six equal faces. Cubes are most often seen in cardboard boxes or dice in games.
- Cuboid: This 3D shape is a solid rectangular structure with 12 edges, eight corners and six rectangular faces. Some examples of cuboids found in everyday life are bricks used in construction, refrigerators in the household, etc.
- Cylinder: This is another 3D shape with two parallel circular bases connected by a curved surface. Examples include soda cans, pipelines, and construction tubes.
- Pyramid: Imagine the shape of a 3D triangle, a pyramid with triangular faces that converge at a point and a polygonal base. The Egyptian pyramids are the most famous example of this shape.
- Sphere: A 3D circle, a sphere is a perfectly round shape seen in various sporting equipment such as cricket balls, tennis balls, planets, etc.
- Cone: Cones have a circular base and a triangular surface on top. Ice cream cones, birthday party hats, and traffic cones are some objects that we encounter in daily life that are cone-shaped.
From simple 2-dimensional shapes to more advanced 3-dimensional figures, each shape is essential, has different properties, and is applied in various disciplines. Shapes are the building blocks of the physical world around us, and therefore, it is vital to understand various types of shapes to appreciate the design and structure in our surroundings and also apply the knowledge of their properties in practical ways.
Open Shapes
Open Figures
Open figures are incomplete shapes where the starting and ending points do not connect. These figures can be represented using line segments or curves, but they will always show a discontinuity.
Open Geometric Shapes
In our daily lives, we encounter various shapes that resemble three-dimensional geometric forms.
Different Shapes
Beyond the typical examples, we also see objects like traffic cones, Rubik's cubes, pyramids, and more in our surroundings. Below, you can observe representations of these shapes to understand their relationship to geometric forms.
Basic Geometric Shapes
Circle Shape
A circle is one of the simplest and most recognizable shapes, defined as a set of points equidistant from a central point. Found everywhere from wheels to coins, circles are symbols of unity and wholeness. In mathematics, circles have constant curvature and can be described by their radius, diameter, and circumference.
Square
The square is a quadrilateral with four equal sides and right angles. This shape is the foundation of many objects in our daily lives, such as tiles, boards, and boxes. Squares are highly symmetrical, and their equal side lengths make them easy to use in grid-based designs like floor layouts and graph papers.
Triangle Shape
Triangles, the simplest polygon, come in various forms. They can be equilateral, where all sides are equal; isosceles, with two equal sides; or scalene, where all sides have different lengths. Triangles are particularly important in construction, as they provide stability and support for structures like bridges.
Rectangle
Rectangles, like squares, are four-sided shapes with opposite sides that are equal. Rectangles are everywhere in our environment, from windows to books. They offer a practical and versatile shape for packaging, design, and more.
Advanced Geometric Shapes
Pentagon
The pentagon is a five-sided polygon commonly seen in structures and nature. One of the most famous examples is the Pentagon building in the United States, which is named after its shape. In nature, starfish exhibit pentagonal symmetry.
Hexagon
Hexagons are six-sided polygons that are highly efficient for packing and tiling. Bees use hexagons in their honeycombs, maximizing space and strength. Hexagonal shapes also appear in various chemical structures and in design.
Octagon
The octagon is an eight-sided shape frequently used in signs, such as stop signs, and in architecture. The shape’s symmetrical properties make it ideal for various design applications.
Other Polygonal Shapes
Beyond octagons, shapes with more sides, such as decagons (ten sides) and dodecagons (twelve sides), are used in advanced geometry and design. These shapes appear in everything from floor tiles to geometric art.
Three-Dimensional Shapes
Sphere
A sphere is a three-dimensional shape where every point on the surface is equidistant from the center. Spheres are seen in natural objects like planets, as well as man-made items such as balls and globes.
Cube
Cubes are three-dimensional versions of squares, with six equal square faces. They are fundamental in mathematics and design, frequently used in architecture, product design, and art.
Cylinder
A cylinder is a three-dimensional shape with two parallel circular bases connected by a curved surface. Cylinders are commonly found in objects like cans and pipes, making them vital in both manufacturing and storage.
Cone
Cones are shapes with a circular base that tapers to a point. They appear in a variety of contexts, from traffic cones to ice cream cones, and are a key shape in architecture and design.
Real-World Applications of Shapes
Shapes in Nature
Nature is filled with geometric shapes. From the hexagons in honeycombs to the symmetry of a butterfly’s wings, shapes play a crucial role in natural design. Understanding these shapes helps scientists and designers create efficient and beautiful systems.
Shapes in Architecture and Design
Architecture relies heavily on shapes to create functional and aesthetically pleasing buildings. Squares and rectangles form the basis of most structures, while triangles provide strength. In modern design, complex shapes like pentagons and octagons are used to create visually striking buildings.
Shapes in Art and Creativity
Artists have long used shapes to convey ideas and emotions. From the geometric precision of Renaissance architecture to the abstract shapes in modern art, understanding shapes is essential for any creative endeavor.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The most common shapes include circles, squares, rectangles, triangles, and polygons like pentagons and hexagons.
Shapes help develop spatial reasoning, visual perception, and categorization skills in both children and adults.
3D shapes, like cubes and spheres, have depth, whereas 2D shapes, like squares and circles, are flat with only height and width.
You can use everyday objects, flashcards, and drawing activities to make learning shapes fun and interactive for children.
Shape names are essential in geometry, where they help define properties like area, perimeter, and volume, forming the foundation of many mathematical concepts.
Uncommon shapes include polygons with more than eight sides, such as decagons and dodecagons, which are used in advanced mathematical applications.
There are many shapes in geometry, but commonly referenced shapes include circles, squares, rectangles, triangles, pentagons, hexagons, octagons, ellipses, and more.
- Circle
- Square
- Rectangle
- Triangle
- Pentagon
- Hexagon
- Heptagon
- Octagon
- Rhombus
- Trapezoid
- Parallelogram
- Ellipse
Common 3D shapes include cubes, spheres, cylinders, cones, pyramids, rectangular prisms, tetrahedrons, and toruses.
Shapes can be classified into various categories, but typically they are divided into two main types: 2D (two-dimensional) and 3D (three-dimensional) shapes.
- Circle
- Triangle
- Square
- Rectangle
- Pentagon
- Hexagon
- Octagon
- Ellipse
There are five basic shapes: circle, triangle, square, rectangle, and oval. These can be combined and modified to create complex shapes.
A 2D shape, or two-dimensional shape, is a flat shape that has length and width but no depth. Examples include squares, circles, and triangles.
- Cube
- Sphere
- Cylinder
- Cone
- Pyramid
- Rectangular prism
- Tetrahedron
- Torus
- Use physical objects to demonstrate shapes.
- Incorporate visual aids like diagrams and models.
- Engage students with hands-on activities like building shapes with clay or blocks.
- Use technology, such as 3D modeling software, to explore shapes.
The general name for shapes is "geometry," which encompasses both 2D and 3D figures.
Shapes are typically named based on the number of sides they have (e.g., triangle for three sides, quadrilateral for four sides) or their characteristics (e.g., circle for a round shape).
- Circle
- Triangle
- Square
- Rectangle
- Pentagon
- Hexagon
- Octagon
- Ellipse
- Rhombus
- Trapezoid
There is no definitive number of shapes, as they can be created in countless variations and combinations, but commonly recognized geometric shapes are in the dozens.
- Geometric shapes (e.g., circles, squares)
- Organic shapes (e.g., shapes found in nature)
- Abstract shapes (e.g., non-representational forms)
- Complex shapes (e.g., shapes formed by combining basic shapes)
Shapes for kids include simple figures like circles, squares, triangles, and rectangles, often introduced through playful activities and interactive games.
Shapes can be identified by counting their sides, examining their angles, and noting their symmetry. Observing their characteristics helps distinguish between different shapes.
The four major shapes are the circle, square, triangle, and rectangle, as they form the basis for many other shapes.































