
The Theory of Evolution is one of the cornerstones of Modern Biology, offering a scientific explanation for the diversity of life on Earth. It posits that species change over time due to Genetic variation, natural selection, and adaptation.
Charles Darwin, the father of Evolutionary Biology, introduced the concept of natural selection as the primary mechanism driving this process, now known as Darwinism. His groundbreaking work on the evolution of species revolutionised how we understand the history of life and our place in the natural world.
Darwin’s theory continues to evolve with the integration of new scientific discoveries, such as Genetics and Molecular Biology, providing a more complete picture of how life develops and changes.
In this article, we will learn more about the Theory of Evolution, Darwinism, and the difference between the theory of evolution and Darwinism.
Table Of Contents:
Darwinism refers to the set of ideas and principles that Charles Darwin proposed to explain the process of evolution by natural selection. It is essentially a specific application of the broader Theory of Evolution, focusing on how species evolve due to environmental pressures and the survival of organisms with advantageous traits.
Darwinism vs. Modern Evolutionary Theory
Impact of Darwinism
Darwinism refers to Charles Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection, a pivotal concept in understanding how species evolve. Although modern evolutionary theory has expanded upon Darwin’s ideas, his core concepts still serve as the foundation for our understanding of the process of evolution.
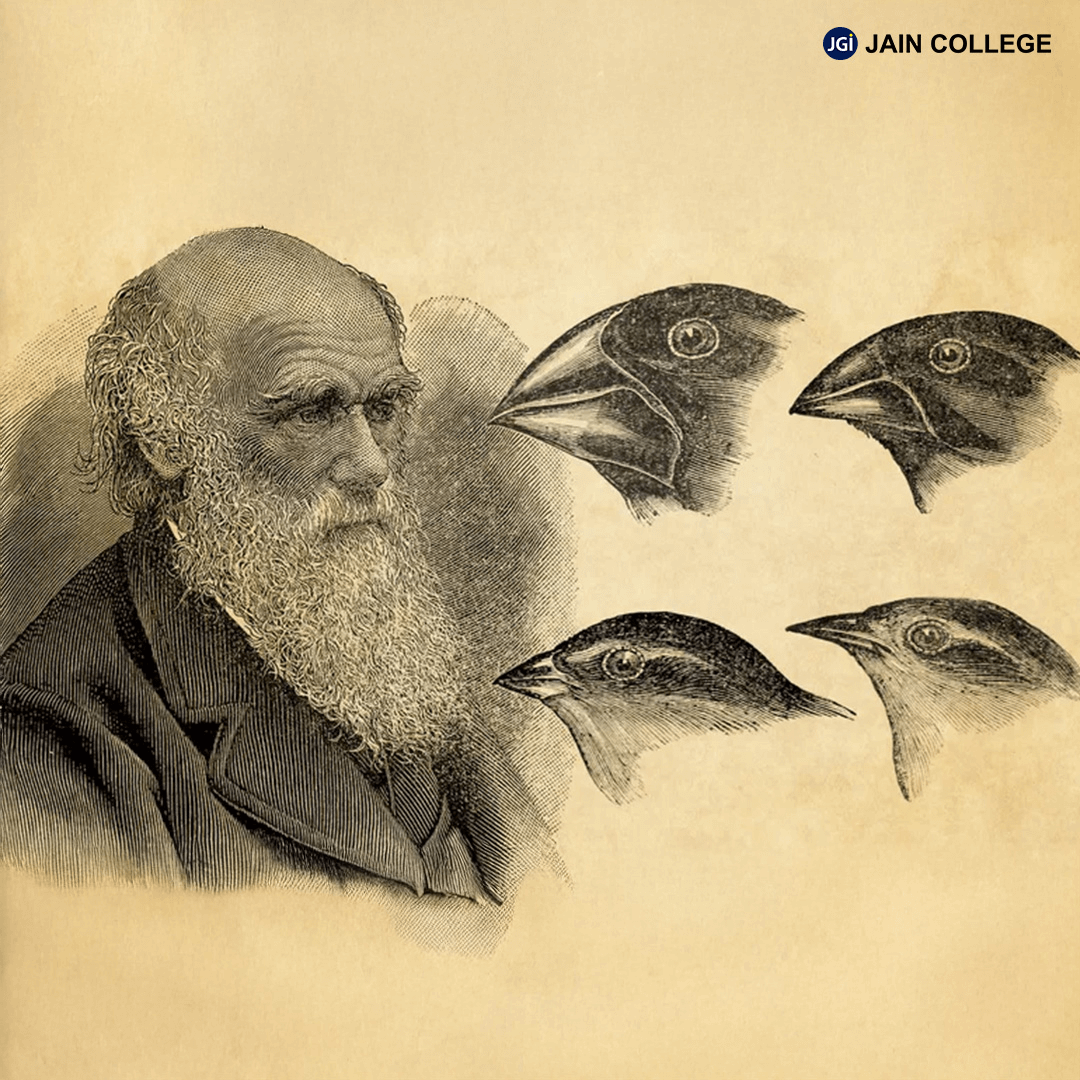
Charles Darwin (1809–1882) was a British naturalist and Biologist whose groundbreaking work on the theory of evolution changed the way we understand the development of life on Earth. His ideas, collectively known as Darwinism, form the foundation of the modern Theory of Evolution.
Darwin is regarded as one of the most influential figures in Science, and his theory of Darwinism laid the groundwork for our understanding of the process of evolution.
While Modern Evolutionary Biology has expanded upon his work with discoveries in Genetics and Molecular Biology, Darwin’s fundamental principles of natural selection and common descent remain at the core of Evolutionary theory today. His ideas continue to shape scientific research and our understanding of life’s diversity on Earth.
Darwin's contribution to science was pivotal in explaining the natural world through a process of evolution rather than supernatural creation.
Charles Darwin:
Early Life and Education: Darwin was born in England and initially studied Medicine before moving to Theology. His interest in Natural History grew during his time at the University of Edinburgh, and later while studying at Cambridge University.
Voyage of the HMS Beagle: Between 1831 and 1836, Darwin sailed around the world aboard the HMS Beagle. His observations of species in different regions, particularly the Galápagos Islands, were instrumental in shaping his evolutionary ideas.
Influences: Darwin was influenced by earlier naturalists like Jean-Baptiste Lamarck, Alfred Russel Wallace, and Charles Lyell (geologist). However, it was Darwin who most clearly articulated the mechanisms of evolution.
Darwinism:
Darwinism refers to the theory of evolution by natural selection that Darwin proposed, explaining how species change over time due to advantageous traits being passed down to successive generations.
The term Darwinism was coined by Thomas Henry Huxley in his March 1861 review of On the Origin of Species, and by the 1870s it was used to describe a range of concepts of evolution or development, without any specific commitment to Charles Darwin's theory of natural selection.
Key Contributions of Darwin:
A. On the Origin of Species (1859)
Darwin's most famous work, "On the Origin of Species," laid out the theory of evolution through natural selection. It was controversial at the time, as it contradicted the dominant belief in creationism—the idea that species were created by a divine being in their current form.
B. Evidence for Evolution
Darwin’s observations in the Galápagos Islands and his study of species variation in different geographical areas led him to propose that species adapt to their environments over time.
He also found fossil evidence and comparative anatomy, showing how species share common structures (e.g., vertebrate limbs), supporting the idea of common ancestry.
Darwinism in Modern Context
While Darwin’s original theory of evolution by natural selection has evolved, it is still considered the foundation of Evolutionary Biology. In modern science, Darwinism has been expanded to include other mechanisms of evolution, such as:
Controversies and Criticisms
Despite the broad acceptance of Darwinism in the scientific community, it has faced criticism from various quarters:
Religious Criticism: Many religious groups reject Darwin's theory, believing in creationism or intelligent design as alternatives to natural selection.
Incomplete Knowledge: At the time, Darwin didn’t have knowledge of Genetics, and his theory was incomplete without understanding how traits are inherited at the molecular level. The discovery of Mendelian Genetics helped clarify and strengthen the theory.
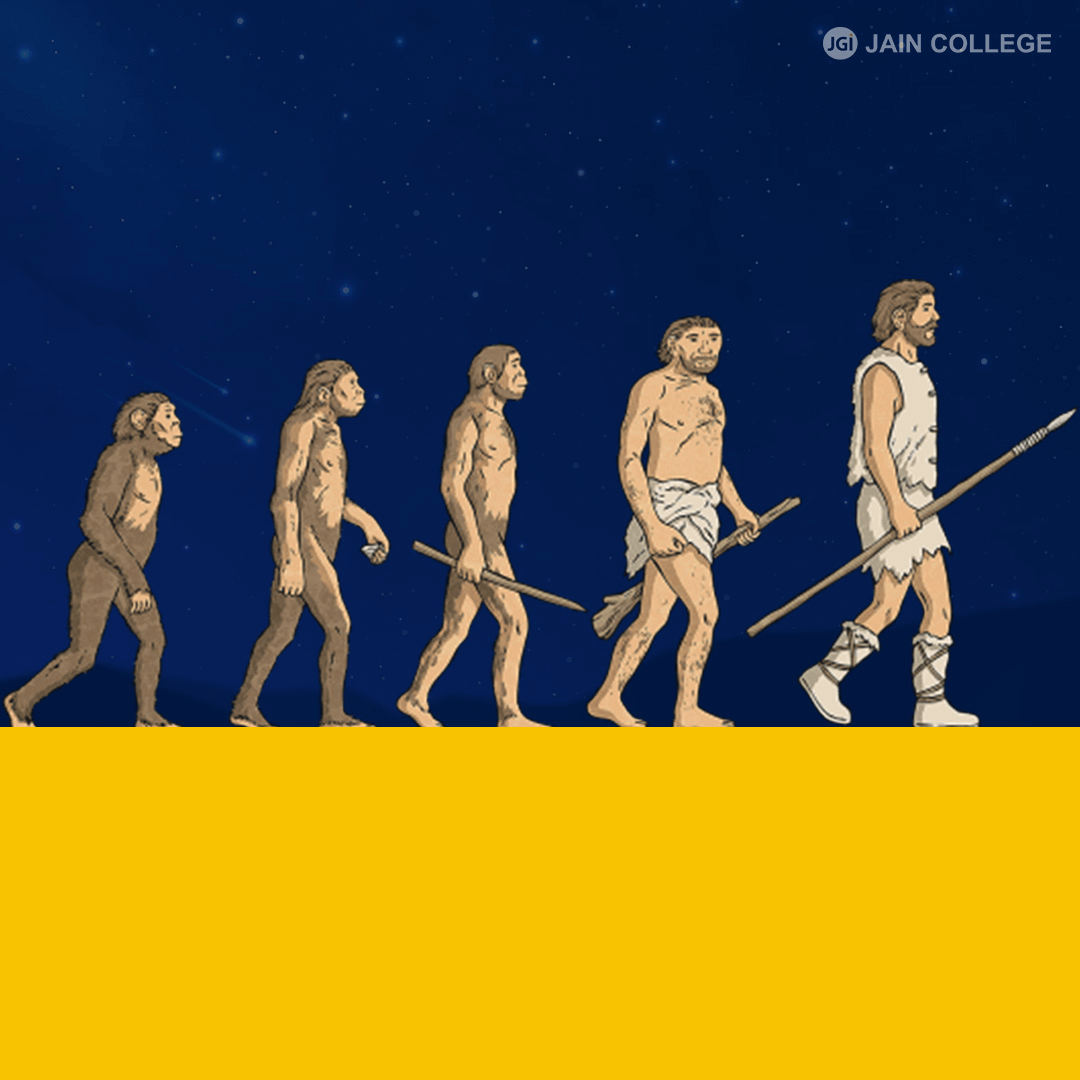
The Theory of Evolution is a scientific concept that explains species changing over time through a process of gradual modification and adaptation to their environment.
The theory asserts that all life forms on Earth share a common ancestor and have evolved through mechanisms like natural selection, Genetic variation, and adaptation. This idea provides a framework for understanding the diversity of life and how species have become suited to their environments.
Key Principles of the Theory of Evolution:
Common Descent
All living organisms are connected through a shared ancestry. Over millions of years, species have evolved from common ancestors into the wide range of organisms we see today.
Natural Selection
Organisms with favourable traits that help them survive in their environment are more likely to reproduce and pass those traits to the next generation. Over time, these advantageous traits become more common in the population.
Genetic Variation
Within any species, there is Genetic diversity (mutations, recombination, etc.). This variation provides the raw material for natural selection to act upon.
Adaptation
Organisms gradually develop traits that help them survive in their specific environments. Over generations, these traits can become so widespread that they define the species.
Speciation
Over time, populations of the same species that are isolated (due to geographic, environmental, or behavioural factors) may evolve into distinct species. This process is known as speciation.
Mechanisms of Evolution:
Also Read: Human Evolution
While the Theory of Evolution and Darwinism both explain how species change over time, there are key distinctions between the two concepts. These differences stem from the scope and mechanisms of evolution that each term refers to.
Darwinism refers to Charles Darwin’s original theory of evolution based primarily on the process of natural selection. Darwinism laid the foundation, modern evolutionary theory has expanded and refined Darwin's ideas to include a variety of mechanisms that drive the complexity of evolution in the natural world.
The Theory of Evolution, however, is a much more comprehensive concept that includes various mechanisms of evolutionary change discovered since Darwin’s time, such as genetics and mutations.
Learn more in detail about the Difference Between the Theory of Evolution and Darwinism:
Theory of Evolution Vs Darwinism
| Theory of Evolution | Darwinism |
| Scope of the Concept | |
| Scope Broad, includes all mechanisms of evolution. | Focuses mainly on natural selection. |
| Mechanisms of Evolution | |
| Includes natural selection, mutations, Genetic drift, gene flow, etc. | Primarily natural selection. |
| Scientific Basis | |
| Integrates Genetics, Molecular Biology, and Modern Discoveries. | Based on Darwin's observations before Genetics was discovered. |
| Current Status | |
| Accepted as the unified theory of evolution. | Considered a historical concept, largely replaced by modern theory. |
| Evolutionary Changes | |
| Gradual accumulation of changes and speciation over time. | Emphasis on gradual changes through natural selection. |
The main difference between both evolution theories is that Darwinism supports natural selection. Meanwhile, Lamarckism supports a vital internal force present in living organisms. They both had different theories about evolution.
Some significant differences between Lamarck’s and Darwin’s evolution theories are:
| Lamarck’s Theory of Evolution | Darwin’s Theory of Evolution |
| Origin of Life | |
| Permanent spontaneous generations | Derived from an ancestral form |
| Driver for Evolution | |
| Evolution of complexities with time | Natural selection |
| Modifications | |
| The adaptation of an organism to its environment | Spontaneous Variations transmitted to the progeny |
| Species Extinction | |
| No, species extinction does not occur | Yes, species extinction occur |
The Theory of Evolution and Darwinism have reshaped our understanding of Biology, demonstrating that life on Earth is not static but ever-changing through natural selection and adaptation.
Darwin’s insights into the evolutionary process have influenced numerous scientific fields, from Genetics to Paleontology, and continue to guide research today. While modern evolutionary theory has expanded upon Darwin’s original ideas by incorporating more mechanisms of evolution, such as Genetic drift and mutations, the core principles of natural selection remain central to our understanding of how species evolve.
Darwin's theory is not just a fundamental Biological concept but also a reminder of the interconnectedness of all life forms, showing how species evolve in response to their environment, leading to the incredible diversity we see today.
Stay tuned @ JAIN PU College to explore human evolution in more detail.
The Theory of Evolution explains how species change over time due to Genetic variations and natural selection. It proposes that all living organisms share a common ancestor and evolve through gradual changes driven by environmental pressures, survival advantages, and reproduction.
Darwinism refers to Charles Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection. It emphasises how species evolve as individuals with advantageous traits (better suited for survival) are more likely to reproduce and pass on those traits.
Darwin developed his theory after extensive observation during his voyage on the HMS Beagle. He studied species, particularly on the Galápagos Islands, noting how animals adapted to different environments. These observations led him to propose that species evolve through natural selection.
Natural selection is the process where organisms with traits that are better suited to their environment have a higher chance of survival and reproduction. Over time, these advantageous traits become more common in the population.
Natural selection operates by favouring individuals with traits that give them a survival advantage in their environment (e.g., faster runners, and better camouflage). These individuals are more likely to survive, reproduce, and pass these traits to their offspring.
The Theory of Evolution refers to the general process of how species change over time, including all mechanisms of evolutionary change (natural selection, mutations, Genetic drift).
Darwinism is specifically focused on natural selection as the main driver of evolution, based on Darwin’s observations and conclusions.
The theory is supported by multiple lines of evidence, including:
While Darwinism focused on natural selection as the main mechanism of evolution, modern evolutionary theory incorporates Genetics, mutations, genetic drift, and gene flow as additional mechanisms. It is now known that evolution is driven by a combination of these factors.
No. While natural selection is a major driver of evolution, other mechanisms like Genetic drift (random changes in gene frequency), gene flow (exchange of genes between populations), and mutations (random genetic changes) also play important roles.
No. Darwin did not understand the genetics behind inheritance. His theory was developed before Mendelian genetics was discovered. However, Modern Evolutionary Biology integrates Darwin's ideas with genetics to explain how traits are passed down through generations.
Darwin’s theory applies to all species, including humans. He proposed that humans evolved through a process of natural selection from earlier hominins and shared a common ancestor with other primates. Human evolution is a key example of Darwin’s ideas in action.
Darwin’s theory challenged existing beliefs in creationism, suggesting that species are not fixed but change over time. It provided a naturalistic, scientific explanation for the diversity of life and laid the foundation for the field of Evolutionary Biology.

JAIN PU College, a part of the renowned JGI Group, is committed to empowering students with quality education.
Beyond academics, the college ensures its online content reflects the same standard of excellence. Every blog and article is meticulously vetted and proofread by subject matter experts to ensure accuracy, relevance, and clarity. From insightful educational topics to engaging discussions, JAIN PU College's content is crafted to inform, inspire, and add value to its readers, reflecting the institution's commitment to intellectual growth and innovation.
View all Blogs