
Ever looked up at the night sky and marveled at the stars? Have you ever wondered what lies beyond the clouds and the familiar layers of our atmosphere?
The mesosphere is one of Earth's least understood yet most essential atmospheric layers. Positioned between the stratosphere and the thermosphere, this cold, dynamic region plays a vital role in meteor destruction, atmospheric circulation, and temperature regulation. Let’s explore the mesosphere facts- structure, composition, significance, and intriguing mesosphere characteristics.
The mesosphere is the third layer of Earth's atmosphere, extending from approximately 50 km (31 miles) to 85 km (53 miles) above sea level. It lies above the stratosphere and below the thermosphere. This layer is significant because it serves as Earth’s primary defense against meteoroids, breaking them apart before they can reach the surface.
Unlike the stratosphere, where commercial airliners cruise, the mesosphere is characterized by decreasing temperatures with altitude, making it the coldest layer of our atmosphere. The upper boundary of this layer is known as the mesopause, where temperatures can plummet to around -143°C (-225°F).
The mesosphere plays a vital role in Earth's atmospheric system, protecting against meteors, influencing upper-atmosphere dynamics, and showcasing some of the coldest temperatures on the planet.
The Mesosphere contains a mixture of gases similar to the lower atmospheric layers but with much lower density and air pressure.
| Gas | Percentage (%) |
| Nitrogen (N₂) | ~78% |
| Oxygen (O₂) | ~21% |
| Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) | ~0.04% |
| Ozone (O₃) | Trace amounts |
The Mesosphere is a crucial atmospheric layer, despite its low air density, as it plays a vital role in meteor destruction and upper-atmosphere dynamics.
The lower boundary is called the stratopause, while the upper boundary is defined by the mesopause.
The mesosphere is Earth's first line of defense against meteors and space debris. As meteoroids enter the atmosphere at high velocities, friction with air molecules in the mesosphere causes them to heat up and disintegrate, creating the bright flashes we see as meteor showers.
The mesosphere contributes to Earth’s climate regulation by helping to redistribute atmospheric heat. Air movements in this layer, including gravity waves and tides, influence global wind patterns and temperature dynamics in the lower layers.
Noctilucent clouds, or polar mesospheric clouds, are rare, high-altitude clouds composed of ice crystals. They form in the mesosphere at altitudes around 80 km (50 miles), primarily over polar regions. These clouds glow faintly at twilight and serve as indicators of climate change and atmospheric conditions.
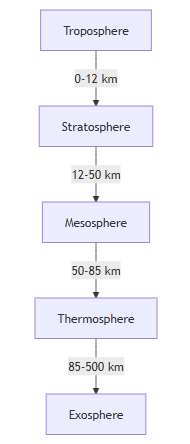
| Atmospheric Layer | Altitude (km) | Temperature Trend | Notable Features |
| Troposphere | 0 - 12 | Decreasing | Weather, breathable air |
| Stratosphere | 12 - 50 | Increasing | Ozone layer, aircraft travel |
| Mesosphere | 50 - 85 | Decreasing | Coldest layer, meteor protection |
| Thermosphere | 85 - 500 | Increasing | Aurora borealis, ISS orbits |
| Exosphere | 500 - 10,000 | Varies | Outer space transition |
graph TD;
A[Troposphere] -->|0-12 km| B[Stratosphere];
B -->|12-50 km| C[Mesosphere];
C -->|50-85 km| D[Thermosphere];
D -->|85-500 km| E[Exosphere];
The mesosphere is far more than just another layer of our atmosphere. It serves as a protective shield against meteors, regulates atmospheric temperatures, and harbors unique noctilucent clouds. Though challenging to study due to its altitude and conditions, ongoing research aims to uncover more about its critical role in Earth's climate system.
The mesosphere protects Earth by burning up meteors before they can impact the surface and helps regulate atmospheric temperatures.
Due to its altitude, the mesosphere receives very little direct heating from the Sun and lacks ozone to trap heat, leading to extreme cold temperatures.
No, aircraft cannot operate in the mesosphere due to low air density, and satellites orbit above it in the thermosphere or exosphere.
Meteors burn up, gravity waves propagate, and noctilucent clouds form, making it a crucial but mysterious atmospheric layer.
Curious to explore more about Earth's atmosphere? Stay tuned for further insights into the wonders of space and science!

JAIN PU College, a part of the renowned JGI Group, is committed to empowering students with quality education.
Beyond academics, the college ensures its online content reflects the same standard of excellence. Every blog and article is meticulously vetted and proofread by subject matter experts to ensure accuracy, relevance, and clarity. From insightful educational topics to engaging discussions, JAIN PU College's content is crafted to inform, inspire, and add value to its readers, reflecting the institution's commitment to intellectual growth and innovation.
View all Blogs