
We are witnessing an increase in the number of nuclear weapons in our modern world. The primary cause of this trend is the increase in geopolitical tensions and significant insecurity. There are currently nine nuclear-armed countries in the world.
The top 9 countries that own the world’s most nuclear weapons in 2025 are:
Let’s learn more in detail about the list of countries with nuclear weapons in 2025.
The nuclear weapon can also be referred to as an atomic weapon, bomb, thermonuclear weapon, or any other explosive device. Nuclear weapons are usually launched from an aircraft, missile, or other platform.
Here's a more detailed breakdown:
Nuclear weapons are the most destructive and the dangerous weapons on earth. These weapons comprise the power to destroy a complete city, potentially resulting in millions of deaths. Thus, they pose a significant threat to the natural environment.
These devices are primarily designed to release energy through nuclear fission, making them explosive in nature. Nuclear weapons derive their destructive force from nuclear reactions and release expansive amounts of energy. Consequently, they have devastating consequences across vast areas.

Nuclear weapons are further categorised into:
Nuclear weapons play a significant role in global military strategy, deterrence theory, and international relations. The control, development, and possession of nuclear weapons are prominent in global security policies and international treaties.
Nuclear weapons are capable of mass destruction, potentially obliterating an entire city, killing millions, and threatening the natural environment as well as future generations due to their long-term catastrophic effects.
The term "proliferation” commonly refers to the increase or spread of nuclear weapons or materials and other destructive military technologies and systems to non-possessing countries.
Some examples of Nuclear Proliferation include:
| 1945 | The Dawn of the Nuclear Age | The United States dropped atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki. Thus, the United States ended World War II and revealed the devastating power of nuclear weapons. |
| 1949 | The Soviet Union Joins the Club | During the Cold War, the USSR successfully tested its first atomic bomb, initiating the nuclear arms race. |
| 1950s–1960s | Spread of Technology | By expanding their list of nuclear powers, the UK, China, and France developed nuclear weapons. The U.S. and the Soviet Union amassed huge arsenals, which fuelled global tension. |
| 1968 | Treaty on the NPT - Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons | It is a landmark international treaty aimed at working toward disarmament, promoting peaceful uses of nuclear energy and preventing the spread of nuclear weapons |
| 1970s–1990s | New Entrants and Challenges | India (1974, “Smiling Buddha” test) and Pakistan (1998) joined the nuclear club, as did Israel (undeclared) and North Korea (2006). This raised regional security concerns. |
| 2000-2025 | Modernisation and New Risks | Nations modernise arsenals; concerns grow over Iran’s nuclear ambitions, North Korea’s tests, and potential nuclear terrorism. |
Many countries worldwide decide either to develop or acquire nuclear weapons mainly because they believe these weapons keep them safe, increase their influence, and help balance power against rivals.
To understand why so many countries possess nuclear weapons, here are a few important reasons:
To understand the total number of nukes in the world, it is important to understand what a nuke is.
The term “NUKE” refers to a nuclear weapon.
Nukes are powerful and extremely destructive devices that use nuclear energy to cause mass destruction.
Nukes are far more powerful and dangerous than regular bombs and can destroy entire cities in seconds. There are two main types of nuclear reactions used in nukes:
Nukes are the most dangerous weapon on Earth. These weapons can cause massive blasts and can flatten entire cities by causing:
Total numbers of Nukes are in the world:
Approximately 12,331 nuclear warheads are known to exist worldwide. Among which:
| Total global warheads: ~12,250 |
| Arsenal in active military hands: ~9,600 |
| Deployed and ready-for-launch: ~3,900 (with ~2,100 on high alert) |
As of 2025, nine countries are known to possess nuclear weapons. These nations fall into two categories: NPT-recognised nuclear weapon states and non-NPT nuclear-armed states.

In general, nuclear-armed countries can be divided into three categories:
Within these categories, countries are typically ranked according to the year of their first successful nuclear test, reflecting nuclear development's historical progression.
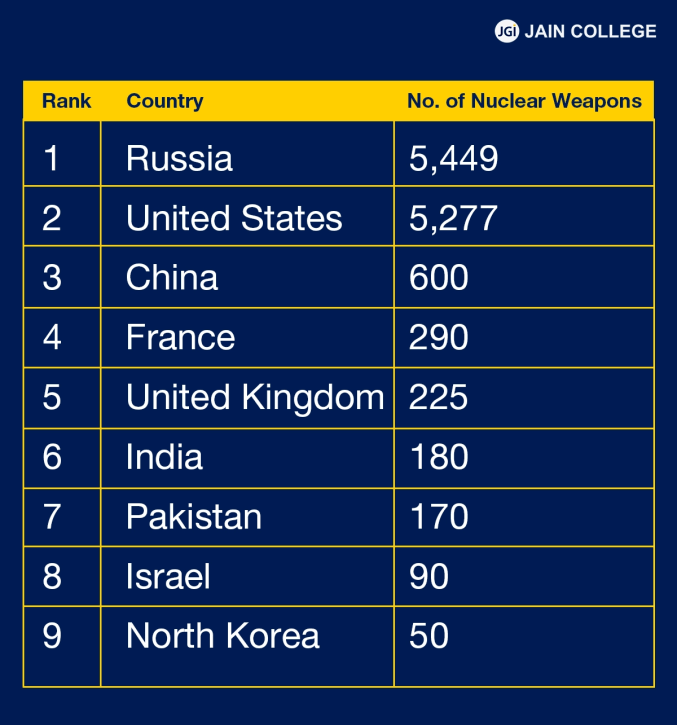
According to ICAN, here is the list of the countries with the most nuclear weapons in the world.
| Rank | Country | No. of Nuclear Weapons |
| 1 | Russia | ~5,449 |
| 2 | United States | ~5,277 |
| 3 | China | ~600 |
| 4 | France | ~290 |
| 5 | United Kingdom | ~225 |
| 6 | India | ~180 |
| 7 | Pakistan | ~170 |
| 8 | Israel | ~90 |
| 9 | North Korea | ~50 |
The Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons is generally known as the Non-Proliferation Treaty or NPT. It is an international treaty aimed at preventing the spread of nuclear weapons and weapons technology. The NPT was designed to promote cooperation in the peaceful use of nuclear energy with the further goal of attaining nuclear deterrence and universal disarmament.
As of 2025, nine countries are known or believed to possess nuclear weapons. These nations fall into two categories: NPT-recognised nuclear weapon states and non-NPT nuclear-armed states.
| Country | NPT Status | Notes |
| Russia | Recognised | Russia possesses the most advanced nuclear weapons worldwide, ranking first among nuclear-powered countries. The country deploys strategic and tactical warheads across air, land, and sea-based platforms as part of its arsenal. |
| United States | Recognised | The United States maintains a modernised nuclear triad:Strategic bombersLand-based missilesSubmarine-launched ballistic missiles |
| China | Recognised | To increase the total number and multiplicity of its warheads, China is particularly focusing on expanding its nuclear forces by designing new missile systems. |
| France | Recognised | France has a fully independent nuclear force. The force primarily operates at sea, using submarine-launched ballistic missiles, supplemented by air-launched weapons. |
| United Kingdom | Recognised | The United Kingdom completely depends on its Triad nuclear deterrence. It is incorporated aboard nuclear-powered submarines. |
| India | Not a member | As part of its deterrence strategy, India adopts a nuclear capability that is maintained at the lowest reasonable level. The country's nuclear policy includes the declaration of NFU (No First Use) doctrines and a focus on secure second-strike capabilities using platforms based on air, land, and sea. |
| Pakistan | Not a member | Pakistan's nuclear posture is largely India-centric and includes developing both short-range tactical weapons and longer-range ballistic missiles. |
| Israel | Not a member | Israel maintains a policy of deliberate ambiguity. It is widely accepted that Israel possesses nuclear weapons, despite its lack of official confirmation. |
| North Korea | Withdrew from NPT | Despite its international sanctions, North Korea resumes expanding its nuclear arsenal. According to reports, its warheads can be delivered via ballistic missiles. |
A comprehensive understanding of the evolving landscape of nuclear weapons is crucial for understanding conversations about security, global peace, and the future of international relations.
According to a study conducted in early 2025 by the Federation of American Scientists (FAS), the total global nuclear warhead count is estimated to be around 12,331.
Nuclear weapons remain a key element of national defence in these states; ongoing modernisation efforts and emerging geopolitical tensions underscore the persistent risks of nuclear proliferation and conflict.
Would you like to explore anything else about "Nuclear Weapons"?
Stay tuned with JAIN PU College- Best PU College in Bangalore and explore in detail about nuclear weapons and their consequences.
The Federation of American Scientists' 2025 status of the world nuclear forces report states that nine countries possess approximately 12,331 nuclear warheads, including over 9,600 in active military stockpiles.
Russia holds the largest nuclear stockpile globally, estimated to possess 5,449 nuclear weapons.
Russia possesses the largest nuclear weapons stockpile in the world, with over 5,500 nuclear warheads. Thus, Russia is ranked number one in nuclear weapons.
Russia, the United States, China, France, and the United Kingdom are known as the top five nuclear superpowers based on their nuclear arsenals and strategic capabilities.
The United States is considered the king of nuclear weapons because of its global reach, its advanced arsenal, and its large number of nuclear tests.
The Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT) officially recognises the following five countries as nuclear-weapon states:
These four countries have developed nuclear weapons, but they are not recognised under the NPT (Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty).

JAIN PU College, a part of the renowned JGI Group, is committed to empowering students with quality education.
Beyond academics, the college ensures its online content reflects the same standard of excellence. Every blog and article is meticulously vetted and proofread by subject matter experts to ensure accuracy, relevance, and clarity. From insightful educational topics to engaging discussions, JAIN PU College's content is crafted to inform, inspire, and add value to its readers, reflecting the institution's commitment to intellectual growth and innovation.
View all Blogs