
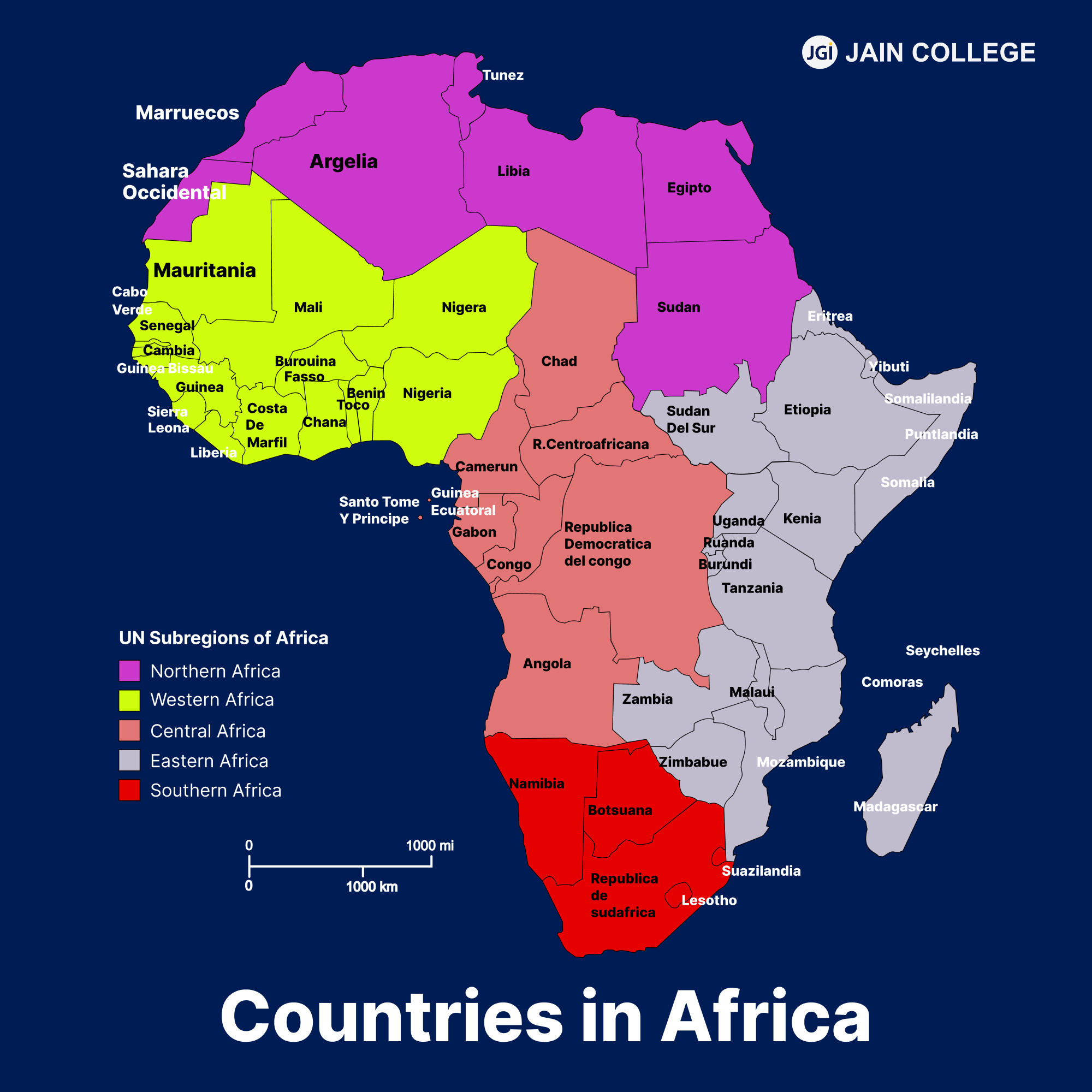
Africa has 54 countries in total. Algeria is the largest by land area, while Nigeria has the largest population. Additionally, Western Sahara and Somaliland are regions with disputed independence. Africa is divided into five main regions: North Africa, West Africa, Central Africa, East Africa, and Southern Africa
Spanning approximately 30.37 million square kilometers (11.7 million square miles), Africa is home to some of the most breathtaking landscapes and ecosystems in the world. A detailed African countries map reveals its five distinct regions:
|
Region |
Description |
Notable Countries |
|
Northern Africa |
Encompasses countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea. |
Egypt, Algeria, Libya, Morocco, Sudan, Tunisia |
|
West Africa |
A region rich in history and culture, known for its dynamic cities and historical sites. |
Nigeria, Ghana, Senegal, Côte d'Ivoire, Mali |
|
East Africa |
Known for its stunning landscapes and wildlife, including famous safari destinations. |
Kenya, Tanzania, Ethiopia, Uganda, Rwanda |
|
Central Africa |
Home to dense rainforests and vast biodiversity, with significant river systems and wildlife. |
Democratic Republic of the Congo, Cameroon, Gabon |
|
Southern Africa |
Characterized by diverse geography and mineral wealth, including deserts, mountains, and savannas. |
South Africa, Namibia, Botswana, Zambia, Zimbabwe |
|
Fact |
Details |
|
Total Number of Countries |
54 recognized sovereign states |
|
Largest Country by Area |
Algeria (2,382,000 km²) |
|
Smallest Country by Area |
Seychelles (459 km²) |
|
Most Populous Country |
Nigeria (over 200 million people) |
Northern Africa is home to some of the oldest civilizations in human history. Egypt, with its legendary pyramids and the Nile River, remains a global tourism hub. Morocco and Tunisia boast a blend of Arab, Berber, and European influences, while Algeria and Libya showcase vast desert landscapes and ancient ruins.
West Africa is famous for its rich cultural heritage, dynamic cities, and historical sites. Nigeria, the region’s economic powerhouse, is known for its booming tech industry and Nollywood films. Ghana attracts visitors with its coastal forts and warm hospitality. Senegal, with its vibrant capital Dakar, offers a lively music and arts scene.
East Africa is a paradise for nature lovers. Kenya and Tanzania are world-renowned for their safari destinations, such as the Serengeti and Masai Mara. Ethiopia, the only African nation never colonized, is known for its ancient churches and unique cuisine. Uganda and Rwanda provide incredible opportunities for gorilla trekking.
Central Africa is home to some of the most biodiverse ecosystems on the planet. The Democratic Republic of the Congo boasts the Congo River and dense rainforests teeming with wildlife. Gabon and Cameroon offer pristine national parks and thriving cultural traditions.
Southern Africa is known for its mineral wealth and scenic beauty. South Africa is a major economic hub, home to Cape Town, Johannesburg, and the iconic Kruger National Park. Botswana and Namibia offer spectacular desert landscapes, while Zimbabwe and Zambia share the awe-inspiring Victoria Falls.
Africa is synonymous with incredible wildlife. From the Big Five (lion, elephant, buffalo, leopard, rhinoceros) to the Great Migration in the Serengeti, the continent offers unparalleled biodiversity.
With thousands of ethnic groups and languages, Africa is a melting pot of traditions. Ancient sites such as the Great Pyramids of Giza, Timbuktu’s manuscripts, and Lalibela’s rock-hewn churches provide deep historical insights.
Africa is rich in natural resources, including gold, diamonds, and oil. Countries like Nigeria, Angola, and South Africa are major players in the global economy due to their mining and energy industries.
Africa has 54 countries in total. Algeria is the largest by land area, while Nigeria has the largest population. Additionally, Western Sahara and Somaliland are regions with disputed independence. Africa is divided into five main regions: North Africa, West Africa, Central Africa, East Africa, and Southern Africa.
A North African nation bordering the Mediterranean Sea, Algeria is the largest country in Africa by area. It features vast desert landscapes and ancient ruins, along with significant oil and gas reserves that play a crucial role in its economy.
Straddling northeast Africa and the Middle East, Egypt is famed for its ancient civilization and iconic monuments like the Giza pyramids. The Nile River sustains agriculture and life, making it a pivotal country for tourism and culture.
Situated on the Mediterranean coast, Libya has significant oil reserves, but it has been marked by political instability and conflict. The nation is working towards peace and reconstruction, focusing on governance and economic recovery.
This North African kingdom boasts both Atlantic and Mediterranean coastlines and blends Arab, Berber, and European influences. Known for tourism and its phosphate industry, Morocco is a stable and culturally rich country.
Located in North Africa, Sudan has a rich yet troubled history marked by internal conflicts and humanitarian crises. The country is now focused on peacebuilding, economic development, and resolving governance challenges.
On the Mediterranean coast, Tunisia is noted for its historical sites and role as the birthplace of the Arab Spring. With tourism as a key sector, Tunisia aims to strengthen its democratic institutions.
A West African nation with a coastline on the Gulf of Guinea, Benin has an economy driven by agriculture and regional trade. The country is known for its cultural traditions, including Vodun, and is working to enhance its economic stability.
This landlocked West African country faces challenges such as poverty, climate change, and political instability. With cotton as a primary export, Burkina Faso is seeking pathways to sustainable development.
An island nation off the coast of West Africa, Cape Verde relies on tourism to fuel its economy. Known for its stable democracy and stunning landscapes, it is a notable destination for travelers.
A major producer of cocoa, Côte d’Ivoire is a West African nation with a rich cultural heritage. It is focused on economic diversification and infrastructure development to bolster its growth.
Situated in West Africa, Ghana is known for its natural resources, including gold and cocoa, and its stable democracy. Its warm hospitality and coastal forts attract numerous tourists.
This West African nation is rich in mineral resources, particularly bauxite, but it struggles with poverty and political instability. Guinea is focused on leveraging its resources for sustainable development.
A small West African nation, Guinea-Bissau has faced political instability and economic challenges. Cashew nuts are a vital export, and regional support is essential for its development.
Founded by freed American slaves, Liberia is a West African nation with a unique history. Recovering from civil conflict, the country faces ongoing development and health challenges.
This landlocked West African nation has a rich cultural history and faces significant challenges related to poverty, drought, and insecurity. Its ancient cities and cultural traditions draw many visitors.
With a vast area covered by the Sahara Desert, Mauritania is a West African country reliant on iron ore and fishing. It is strategically focused on counter-terrorism efforts in the Sahel region.
A landlocked nation in West Africa, Niger faces severe challenges due to desertification, food insecurity, and poverty. International aid plays a vital role in supporting its population.
As the most populous country in Africa and a major oil producer, Nigeria is a vibrant nation with a booming tech industry and a prominent film sector known as Nollywood.
Located in West Africa, Senegal is known for its stable democracy, diverse culture, and dynamic capital city, Dakar. Tourism and fishing contribute significantly to its economy.
This West African nation is recovering from a civil war and the Ebola outbreak, facing significant health and development challenges. It has rich mineral resources, including diamonds.
Surrounded by Senegal, The Gambia is the smallest country on mainland Africa and relies on tourism to support its economy. The country has experienced a peaceful transition to democracy.
A small West African nation with a narrow coastline, Togo's economy depends on agriculture, phosphate resources, and trade. It seeks regional integration and investment to boost economic growth.
Situated in Central Africa, Angola is a major oil producer that is rebuilding after a prolonged civil war. The country is focused on diversifying its economy and improving governance and infrastructure.
This Central African nation is known for its diverse geography and cultural traditions. Its economy is based on agriculture, and it is striving for greater national unity and stability.
A landlocked nation in Central Africa, the Central African Republic is facing severe poverty and political instability. It requires significant humanitarian assistance to address its challenges.
A landlocked country in Central Africa, Chad faces severe challenges related to desertification, poverty, and political instability. The nation's economy is largely based on agriculture and livestock.
Encompassing a vast area in Central Africa, the Democratic Republic of Congo is rich in natural resources but faces significant security and governance challenges.
A small nation on the coast of Central Africa, Equatorial Guinea is one of the continent's largest oil producers. It has a high per capita income but is working to improve human rights and social development.
Located in Central Africa, Gabon is known for its oil resources and extensive rainforests, which contribute to a high per capita income. The country seeks economic diversification and sustainable development.
This Central African nation relies on oil revenues and has experienced periods of political instability. It seeks to diversify its economy and promote regional cooperation.
A landlocked nation in East Africa, Burundi faces challenges related to overpopulation, poverty, and political instability. Agriculture is central to its economy
An island nation off the coast of East Africa, the Comoros relies on agriculture and fishing. It has experienced political instability and is focused on attracting investment in tourism.
Strategically located in the Horn of Africa, Djibouti relies on its port and logistics sectors. Hosting foreign military bases has made it a key player in regional stability.
Situated in the Horn of Africa, Eritrea maintains a closed political system and faces economic and human rights challenges. It has a strategic location along the Red Sea.
In East Africa, Ethiopia is known for its ancient history, diverse cultures, and rapid economic growth. It is a major agricultural producer and a key player in the African Union.
Located in East Africa, Kenya is renowned for its wildlife, tourism, and dynamic economy. Nairobi serves as a major regional hub for trade, finance, and technology.
This island nation off the coast of East Africa is known for its unique biodiversity. It faces challenges related to poverty and deforestation, focusing on sustainable development.
A landlocked nation in Southeast Africa, Malawi faces challenges related to poverty, food insecurity, and HIV/AIDS. Agriculture is a mainstay of its economy.
An island nation off the coast of East Africa, Mauritius has a diversified economy and a stable democracy, making it a regional success story. Tourism and financial services are crucial.
Located in Southeast Africa, Mozambique has a long coastline and rich natural resources, including natural gas. However, it faces poverty and security challenges.
An East African nation recovering from genocide, Rwanda has made significant progress in economic development and technology. It is focused on sustainable growth and stability.
An archipelago off the coast of East Africa, the Seychelles relies on tourism and fishing. Its natural beauty and high per capita income make it a unique destination.
Facing prolonged conflict and humanitarian crises, Somalia seeks to rebuild its government and economy amidst piracy and terrorism challenges.
As the world's newest nation, South Sudan faces enormous challenges related to security, governance, and economic stability. It is rich in oil but suffers from ongoing conflict.
Known for its wildlife, including the Serengeti and Mount Kilimanjaro, Tanzania is a key destination for tourism. Agriculture also plays a crucial role in its economy.
In East Africa, Uganda has diverse geography and fertile lands, supporting a primarily agricultural economy. It seeks to enhance regional trade and attract investment.
Landlocked in Southern Africa, Botswana is known for its diamond industry and good governance. The country strives for economic diversification and sustainable development.
A small, landlocked nation in Southern Africa, Eswatini maintains a monarchy and focuses on agriculture and manufacturing. It is working to address poverty and health challenges.
Enclaved within South Africa, Lesotho relies on remittances and agriculture. The mountain kingdom faces challenges related to poverty and environmental degradation.
Characterized by desert landscapes and rich mineral resources, Namibia focuses on mining and tourism. It strives for balanced economic growth and environmental sustainability.
As a major economic hub in Southern Africa, South Africa has diverse landscapes, including the iconic Kruger National Park and Cape Town. It deals with significant economic inequality.
Landlocked in Southern Africa, Zambia's economy relies heavily on copper. The country aims to diversify its economy and improve living standards for its population.
Located in Southern Africa, Zimbabwe has faced political and economic instability. It seeks economic recovery through agriculture, mining, and regional cooperation.
Africa is a continent of unparalleled diversity, offering a wealth of experiences in culture, history, and nature. Whether you are exploring the ancient pyramids of Egypt, embarking on a safari in Kenya, or enjoying the coastal beauty of Seychelles, Africa has something for everyone. With 54 nations to discover, this guide serves as your comprehensive resource for exploring Africa’s countries and planning your next adventure.
There are 54 countries in Africa today, as recognized by the United Nations. The full list of countries, along with their current population and subregion, is provided in the table below based on the latest official United Nations statistics.
The biggest countries in Africa by land size are Algeria, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Sudan, Libya, Chad, Niger, Angola, Mali, South Africa, Ethiopia
The regions of Africa include: Northern Africa, Western Africa, Central Africa, Eastern Africa, Southern Africa, and the Horn of Africa, with countries like Algeria, Egypt, Morocco, Nigeria, Kenya, South Africa, Ethiopia, and Democratic Republic of Congo falling under these respective categories.
Seychelles is the smallest African country by area.
Africa is renowned for its wildlife, rich cultural heritage, and stunning landscapes. Delve deeper into the diverse countries of Africa now! Keep an eye on our blog for more insights like these!
The second largest country in Africa by land area is the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
The largest country in Africa by land area is Algeria.
The smallest country in Africa by land area is Seychelles.
Nigeria has the highest population in Africa.
Nigeria has the largest economy in Africa, based on GDP.
Madagascar has the longest coastline in Africa.
Madagascar has the longest coastline in Africa.
The Democratic Republic of the Congo is considered one of the richest in natural resources.
Nigeria is known as the "Giant of Africa" due to its large economy and population.
Ethiopia is considered one of the oldest countries in Africa
Nigeria has the highest number of spoken languages, with over 500.
South Africa has the most UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Africa.
Egypt is ranked as having the strongest military in Africa.
Morocco is one of the most visited countries in Africa.
Algeria is home to the largest portion of the Sahara Desert.
Tanzania has the tallest mountain, Mount Kilimanjaro.
Lake Victoria, shared by Uganda, Kenya, and Tanzania, is the largest lake in Africa.
Mauritius is often ranked as the safest country in Africa
Ethiopia has one of the fastest-growing economies in Africa.
Kenya and South Africa are famous for their diverse wildlife and safari tourism.

JAIN PU College, a part of the renowned JGI Group, is committed to empowering students with quality education.
Beyond academics, the college ensures its online content reflects the same standard of excellence. Every blog and article is meticulously vetted and proofread by subject matter experts to ensure accuracy, relevance, and clarity. From insightful educational topics to engaging discussions, JAIN PU College's content is crafted to inform, inspire, and add value to its readers, reflecting the institution's commitment to intellectual growth and innovation.
View all Blogs