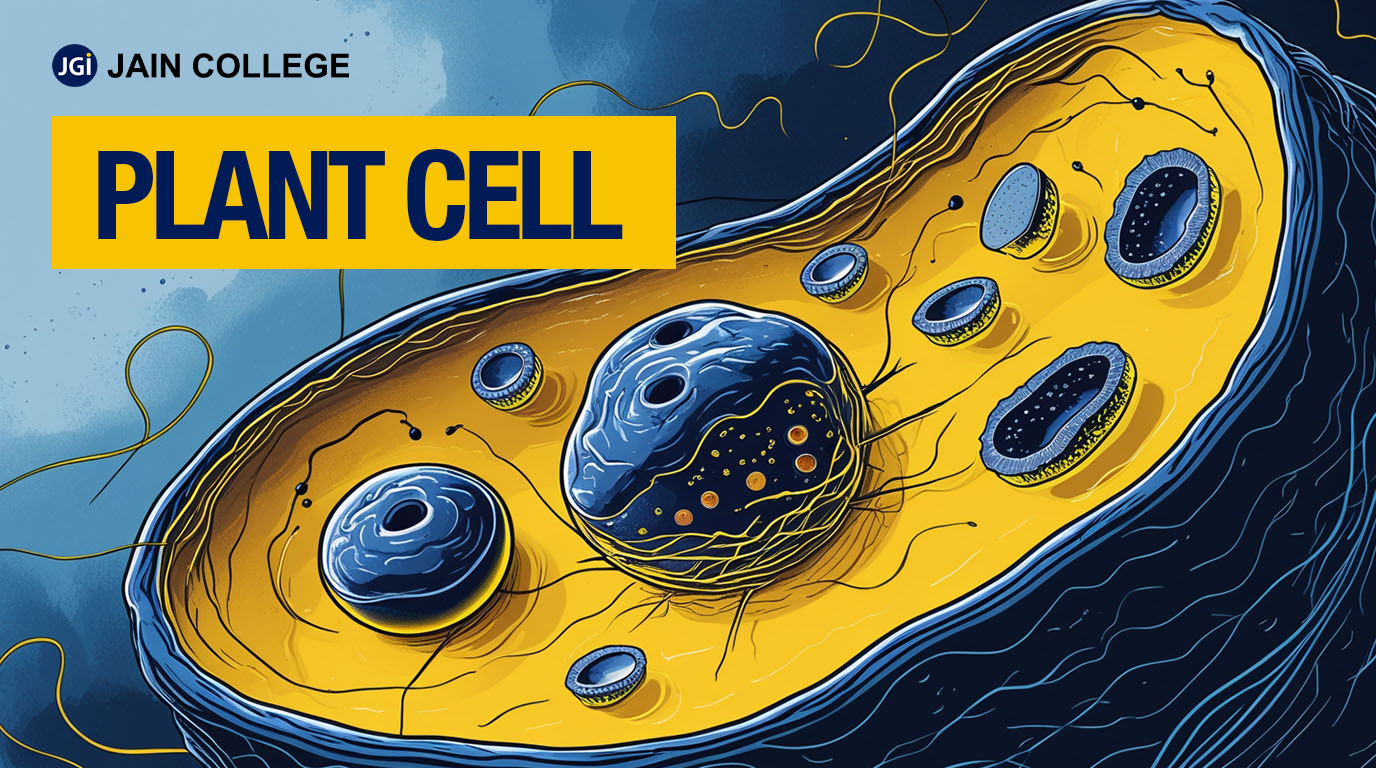
Unique Features of Plant Cells
Organelles and Their Functions
Role of the plant cell within the plant
“All life on Earth is made from cells. Without cells, there can be no life.” – BBC Blog.
While bacteria are single-celled or unicellular organisms, plants are made of a multitude of cells and are called multicellular organisms. Every cell has a different function and is hence referred to as a specialised cell.
Each plant cell is a fascinating world within itself, teeming with structures and functions that are vital for the survival and growth of plants. Understanding the plant cell can open doors to a deeper appreciation of nature and create a better understanding of a plant’s structure. Through this blog, we will explore the fascinating world of plant cells and their various parts.
Plant cells are the basic units of life in plants. They are eukaryotic, which means they have a defined nucleus and other specialised structures, or organelles, enclosed within membranes. Each plant cell functions like a small factory, working tirelessly to support the plant's life processes.
Plant cells share many characteristics with animal cells; however, they have some unique features that set them apart:
Cell Wall: plant cells have a rigid cell wall made of cellulose. This wall provides structural support, protection, and shape to the cell.
Figure: Structure of a chloroplast
Chloroplasts: These are the sites where photosynthesis occurs, a process through which plants convert sunlight into chemical energy. Chloroplasts are surrounded by an inner membrane that is less permeable and studded with transport proteins and an outer membrane that is permeable to small organic molecules. The innermost matrix of chloroplasts is called the stroma and contains metabolic enzymes and multiple copies of the chloroplast genome. Chloroplasts have a third internal membrane called the thylakoid membrane which contains a green, light-absorbing pigment called chlorophyll. They also have intricate electron transport chains used in photosynthesis.
Vacuole: This is a storage organelle present in the cytoplasm that can occupy up to 90% of the cell's volume. It stores water, nutrients, and waste products, and helps maintain turgor pressure, which keeps the plant upright.
The organelles are specialised structures within the cell that perform specific functions. Some of the organs found in the plant cell besides the cell wall, chloroplast and vacuole are:
Photosynthesis is a remarkable process carried out by plant cells to nourish and energise the plant. When the chlorophyll absorbs energy from blue- and red-light waves, of the sun, it reflects green-light waves that make the plant appear green. In the presence of sunlight, plants take in carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) from the air and soil. Within the plant cell, the water is oxidised as it loses electrons, and the carbon dioxide is reduced as it gains electrons. This process transforms the water into oxygen and the carbon dioxide into glucose. The plant then releases the oxygen into the air, and stores energy within the glucose molecules.
The chemical equation for photosynthesis is:
6CO? + 6H?O + Light Energy → C?H??O? + 6O?
Within a plant, the plant cells perform other functions besides photosynthesis such as:
Plant cells perform a crucial role in the plant by giving it found, creating its structure and transporting nutrients to all parts of the plant. Understanding its nature and functions helps us better understand how plants exist and how they can be nurtured. Understanding plant cells is crucial for multiple reasons:
The plant cell is a remarkable system that embodies efficiency, resilience, and harmony. Understanding its structure and functions helps us understand the life within plants and gain insights into broader biological processes that sustain life on Earth.

JAIN PU College, a part of the renowned JGI Group, is committed to empowering students with quality education.
Beyond academics, the college ensures its online content reflects the same standard of excellence. Every blog and article is meticulously vetted and proofread by subject matter experts to ensure accuracy, relevance, and clarity. From insightful educational topics to engaging discussions, JAIN PU College's content is crafted to inform, inspire, and add value to its readers, reflecting the institution's commitment to intellectual growth and innovation.
View all Blogs